Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 35386912
- PMCID: PMC8977463
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.816656
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
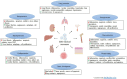
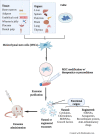
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is rising in global prevalence and has become a worldwide public health problem, with adverse outcomes of kidney failure, cardiovascular disease, and premature death. However, current treatments are limited to slowing rather than reversing disease progression or restoring functional nephrons. Hence, innovative strategies aimed at kidney tissue recovery hold promise for CKD therapy. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are commonly used for regenerative therapy due to their potential for proliferation, differentiation, and immunomodulation. Accumulating evidence suggests that the therapeutic effects of MSCs are largely mediated by paracrine secretion of extracellular vesicles (EVs), predominantly exosomes. MSC-derived exosomes (MSC-Exos) replicate the functions of their originator MSCs via delivery of various genetic and protein cargos to target cells. More recently, MSC-Exos have also been utilized as natural carriers for targeted drug delivery. Therapeutics can be effectively incorporated into exosomes and then delivered to diseased tissue. Thus, MSC-Exos have emerged as a promising cell-free therapy in CKD. In this paper, we describe the characteristics of MSC-Exos and summarize their therapeutic efficacy in preclinical animal models of CKD. We also discuss the potential challenges and strategies in the use of MSC-Exos-based therapies for CKD in the future.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; exosome; mesenchymal stem cells; new advances; regeneration; therapy.
Copyright © 2022 Cao, Huang, Chen and Pollock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles to the Rescue of Renal Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 20;22(12):6596. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126596. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34202940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes in clinical trials.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Apr 7;14(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03287-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37024925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: Toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine.World J Stem Cells. 2020 Aug 26;12(8):814-840. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.814. World J Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 32952861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin-stimulated exosomes enhance the regenerative potential of chronic kidney disease-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells via cellular prion proteins.J Pineal Res. 2020 Apr;68(3):e12632. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12632. Epub 2020 Feb 17. J Pineal Res. 2020. PMID: 31989677
-
A scaffold laden with mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for promoting endometrium regeneration and fertility restoration through macrophage immunomodulation.Acta Biomater. 2020 Sep 1;113:252-266. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.06.029. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32574858
Cited by
-
The Fatal Role of Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli Shiga Toxin-associated Extracellular Vesicles in Host Cells.J Microbiol. 2023 Aug;61(8):715-727. doi: 10.1007/s12275-023-00066-0. Epub 2023 Sep 4. J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37665555 Review.
-
IL-1β-pretreated bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate septic endoplasmic reticulum stress via regulating SIRT1/ERK pathway.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 13;9(10):e20124. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20124. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37771539 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy in Kidney Diseases: Potential and Challenges.Cell Transplant. 2023 Jan-Dec;32:9636897231164251. doi: 10.1177/09636897231164251. Cell Transplant. 2023. PMID: 37013255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Renal Inflammatory Diseases: Revealing Mechanisms of Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Macrophage Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 12;26(8):3646. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083646. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Dental-derived Stem Cell-based Therapy and Their Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Post-COVID-19 Syndrome-induced Tissue Damage.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024 Nov;20(8):2062-2103. doi: 10.1007/s12015-024-10770-y. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024. PMID: 39150646 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

