SARS-CoV-2 Infection Can Lead to an Increase in Tacrolimus Levels in Renal Transplant Patients: A Cohort Study
- PMID: 35387396
- PMCID: PMC8977848
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2022.10127
SARS-CoV-2 Infection Can Lead to an Increase in Tacrolimus Levels in Renal Transplant Patients: A Cohort Study
Abstract
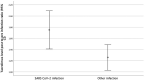
The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection on serum tacrolimus levels. Tacrolimus levels of 34 transplant patients diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 in 2020 were compared with their pre-infection values and those of a control group with alternative infections. 20 out of 34 (59%) had high levels. At diagnosis, median tacrolimus level in the SARS-CoV-2 cohort was 9.6 μg/L (2.7-23) compared to 7.9 μg/L in the control group (p = 0.07, 95% CI for difference -0.3-5.8). The ratio of post-infection to pre-infection tacrolimus values was higher in the SARS-CoV-2 group (1.7) compared to the control group (1.25, p = 0.018, 95% CI for difference 0.08-0.89). The acute kidney injury rate was 65% (13 of 20) in SARS-CoV-2 patients with a level >8 μg/dl, compared to 29% (4 of 14) in those with lower levels (p = 0.037). Median length of stay was 10 days among SARS-CoV-2 infected patients with high tacrolimus levels compared to 0 days in the rest (p = 0.04). Four patients with high levels died compared to 2 in the control group. Clinicians should be aware of this potential effect on tacrolimus levels and take appropriate measures.
Keywords: AKI; SARS-CoV-2; immunosuppression; kidney transplantation; tacrolimus; tacrolimus levels.
Copyright © 2022 Chalklin, Koimtzis, Khalid, Carrington-Windo, Elker and Asderakis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

