Basis of narrow-spectrum activity of fidaxomicin on Clostridioides difficile
- PMID: 35388215
- PMCID: PMC9635844
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04545-z
Basis of narrow-spectrum activity of fidaxomicin on Clostridioides difficile
Abstract
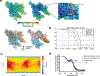
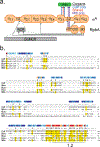
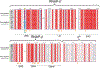
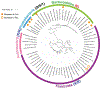
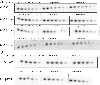
Fidaxomicin (Fdx) is widely used to treat Clostridioides difficile (Cdiff) infections, but the molecular basis of its narrow-spectrum activity in the human gut microbiome remains unknown. Cdiff infections are a leading cause of nosocomial deaths1. Fidaxomicin, which inhibits RNA polymerase, targets Cdiff with minimal effects on gut commensals, reducing recurrence of Cdiff infection2,3. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structure of Cdiff RNA polymerase in complex with fidaxomicin and identify a crucial fidaxomicin-binding determinant of Cdiff RNA polymerase that is absent in most gut microbiota such as Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes. By combining structural, biochemical, genetic and bioinformatic analyses, we establish that a single residue in Cdiff RNA polymerase is a sensitizing element for fidaxomicin narrow-spectrum activity. Our results provide a blueprint for targeted drug design against an important human pathogen.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


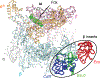


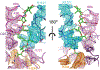


Comment in
-
A roadmap for designing narrow-spectrum antibiotics targeting bacterial pathogens.Microb Cell. 2022 Jul 4;9(7):136-138. doi: 10.15698/mic2022.07.780. eCollection 2022 Jul 4. Microb Cell. 2022. PMID: 35855392 Free PMC article.
References
Methods References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

