Psychological variables in medically assisted reproduction: a systematic review
- PMID: 35388278
- PMCID: PMC8966420
- DOI: 10.5114/pm.2022.114404
Psychological variables in medically assisted reproduction: a systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: The paths of medically assisted reproduction represent the most important scientific progress to cope with the inability to achieve spontaneous conception (SC) and to reach desired parenthood. Couples undergoing assisted reproductive technology (ART) and couples not facing ovulation induction and artificial fertilization show sufficient levels of well-being and psychological adjustment. However, in some cases couples undergoing ART show lower perceived quality of life than couples with SC.Our aim is to investigate the main psychological variables involved in the special risk condition of medically assisted reproduction and how they could direct specific guidelines to enhance mental wellbeing in dealing with infertility.
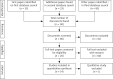
Material and methods: In this regard, we performed a systematic review following the PRISMA guidelines. From all the studies included, the considered outcome measures were psychological, social, and relational variables and are presented in a systematic approach.
Results: A total of 14 studies were included in this article, according to our strict inclusion criteria.
Conclusions: Conflicting results have been proven by this systematic review. Even though all underlined the importance of taking charge of the psychological variables in infertility, few studies monitored and evaluated the effectiveness of these interventions. Moreover, none of the selected studies monitored the evolutionary implications of parental competence on the development of children born from ART.
Keywords: ART; developmental psychology; medically assisted reproduction; psychological wellbeing; quality of life.
Copyright © 2022 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Prapas Y, Petousis S, Panagiotidis Y, et al. . Injection of embryo culture supernatant to the endometrial cavity does not affect outcomes in IVF/ICSI or oocyte donation cycles: a randomized clinical trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2012; 162: 169-173. - PubMed
-
- Gullo G, Petousis S, Papatheodorou A, et al. . Closed vs. Open Oocyte Vitrification Methods are equally effective for blastocyst embryo transfers: Prospective Study from a Sibling Oocyte Donation Program. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2020; 85: 206-212. - PubMed
-
- Papatheodorou A, Vanderzwalmen P, Panagiotidis Y, et al. . How does closed system vitrification of human oocytes affect the clinical outcome? A prospective, observational, cohort, noninferiority trial in an oocyte donation program. Fertil Steril 2016; 106: 1348-1355. - PubMed
-
- Šprem Goldštajn M, Mikuš M, Ćorić M, et al. . The pharmacoeconomic impact of follitropin alpha biosimilars in IVF therapy in Europe: a report of the literature. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res 2021; 21: 553-558. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources