Assessing physical access to healthy food across United Kingdom: A systematic review of measures and findings
- PMID: 35388348
- PMCID: PMC8976549
- DOI: 10.1002/osp4.563
Assessing physical access to healthy food across United Kingdom: A systematic review of measures and findings
Abstract
Background: Existing research suggests that physical access to food can affect diet quality and thus obesity rates. When defining retail food environment (RFE) quantitatively, there is a little agreement on how to measure "lack of healthy food" and what parameters to use, resulting in a heterogeneity of study designs and outcome measures. In turn, this leads to a conflicting evidence base being one of the many barriers to using evidence in policy-making.
Aims: This systematic review aimed to identify and describe methods used to assess food accessibility in the United Kingdom (UK) to overcome heterogeneity by providing a classification of measures.
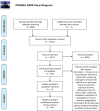
Materials & methods: The literature search included electronic and manual searches of peer-reviewed literature and was restricted to studies published in English between January 2010 and March 2021. A total of 9365 articles were assessed for eligibility, of which 44 articles were included in the review. All included studies were analysed with regards to their main characteristics (e.g., associations between variables of interest, setting, sample, design, etc.) and definition of RFE and its metrics. When defining these metrics, the present review distinguishes between a point of origin (centroid, address) from which distance was calculated, summary statistic of accessibility (proximity, buffer, Kernel), and definition of distance (Euclidean, network distance). Trends, gaps and limitations are identified and recommendations made for food accessibility research in UK.
Results: Multiple theoretical and methodological constructs are currently used, mostly quantifying distance by means of Euclidean and ring-buffer distance, using both proximity- and density-based approaches, and ranging from absolute to relative measures. The association between RFE and diet and health in rural areas, as well as a spatiotemporal domain of food access, remains largely unaccounted.
Discussion: Evidence suggests that the duration of exposure may bear a greater importance than the level of exposure and that density-based measures may better capture RFE when compared with proximity-based measures, however, using more complex measures not necessarily produce better results. To move the field forward, studies have called for a greater focus on causality, individual access and the use of various measures, neighbourhood definitions and potential confounders to capture different aspects and dimensions of the RFE, which requires using univariate measures of accessibility and considering the overall context in terms of varying types of neighbourhoods.
Conclusion: In order to render ongoing heterogeneity in measuring RFE, researchers should prioritise measures that may provide a more accurate and realistic account of people's lives and follow an intuitive approach based on convergence of results until consensus could be reached on using some useful standards.
Keywords: RFE; food access; food desert; obesity.
© 2021 The Authors. Obesity Science & Practice published by World Obesity and The Obesity Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cerin E, Frank LD, Sallis JF, et al. From neighborhood design and food options to residents’ weight status. Appetite. 2011;56(3):693‐703. - PubMed
-
- Clary C, Matthews SA, Kestens Y. Between exposure, access and use: reconsidering foodscape influences on dietary behaviours. Heal Place. 2017;44:1‐7. - PubMed
-
- Wilkins E, Radley D, Morris M, et al. A systematic review employing the GeoFERN framework to examine methods, reporting quality and associations between the retail food environment and obesity. Heal Place. 2019;57:186‐199. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources