Revisiting the Extinction of the RNA World
- PMID: 35389627
- PMCID: PMC9069686
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00121
Revisiting the Extinction of the RNA World
Abstract
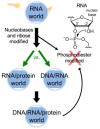
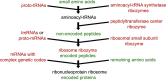
The ribozyme world is thought to have evolved the burdensome complexity of peptide and protein synthesis because the 20 amino acid side chains are catalytically superior. Instead, I propose that the Achilles heel of the RNA world that led to the extinction of riboorganisms was RNA's polyanionic charges that could not be covalently neutralized stably by phosphotriester formation. These charges prevented development of hydrophobic cores essential for integration into membranes and many enzymatic reactions. In contrast, the phosphotriester modification of DNA is stable. So, the fact that the charge was never removed in DNA evolution gives further credence to proteins coming before DNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rich A.On the problems of evolution and biochemical information transfer. In Horizons in biochemistry; Kasha M., Pullman B., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, 1962; pp 103–126.
-
- Grosjean H.Nucleic acids are not boring long polymers of only four types of nucleotides. In DNA and RNA modification enzymes: structure, mechanism, function and evolution; Grosjean H., Ed.; Landes Bioscience: Austin, TX, 2009; pp 1–18.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

