Testing Communication Concepts on COVID-19 Contact Tracing Among Black and Latinx/Hispanic People in the United States
- PMID: 35391715
- PMCID: PMC8989261
- DOI: 10.1007/s40615-021-01167-5
Testing Communication Concepts on COVID-19 Contact Tracing Among Black and Latinx/Hispanic People in the United States
Abstract
Objective: Black and Latinx/Hispanic people were more than twice as likely to die from COVID-19 than White people, but because of legacies of discrimination and maltreatment in health care, were less likely to participate in some public health responses to COVID-19, including contact tracing. This study aimed to test three communication campaign concepts to engage Black and Latinx/Hispanic people in contact tracing efforts.
Methods: Twelve focus group discussions with 5 to 10 participants each were conducted online among participants from Black and Latinx/Hispanic urban populations in Philadelphia and New York state. Participants provided sociodemographic information and were presented with potential campaign concepts and prompted to rate the concepts and engage in open-ended discussion. For rating and sociodemographic data, chi-square tests were performed. For open-ended discussion data, a thematic analysis approach was used.
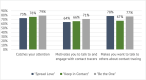
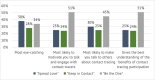
Results: Across groups, the campaign concept that was rated most likely to encourage cooperation with contact tracing efforts was "Be the One," with 45% of total first-place votes. Participants expressed that the campaign caught their attention (79%), motivated them to engage with contact tracers (71%) and to talk to others about contact tracing (77%). Discussions also elucidated: the importance of community engagement; the need for clearer explanations of contact tracing; the preference for already trusted, community-based contact tracers; the need to reassure people about confidentiality; and for contact tracing to be culturally competent and empathetic.
Conclusions: This study highlights how strategic, culturally sensitive communication can buttress current and future contact tracing efforts, especially among Black and Latinx/Hispanic people.
Keywords: Black; COVID-19; Contact tracing; Latinx/Hispanic; Mass media campaign; Racial and ethnic disparities.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yancy CW. COVID-19 and African Americans. JAMA. Published online April 15, 2020. 10.1001/jama.2020.6548 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical