Anti-Myxovirus Resistance Protein-1 Immunoglobulin A Autoantibody in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 35391716
- PMCID: PMC8983265
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1107673
Anti-Myxovirus Resistance Protein-1 Immunoglobulin A Autoantibody in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
Background: We have previously analysed serum autoantibody levels in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (iNSIP), and healthy controls and identified the autoantibody against anti-myxovirus resistance protein-1 (MX1) to be a specific autoantibody in iNSIP. We found that a higher anti-MX1 autoantibody level was a significant predictor of a good prognosis in patients with non-IPF idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. In this retrospective study, we sought to clarify the prognostic significance of the anti-MX1 autoantibody in IPF.
Methods: We measured anti-MX1 immunoglobulin (Ig) G, IgA, and IgM autoantibody levels by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in serum collected at the time of diagnosis from 71 patients with IPF diagnosed according to the 2018 IPF guideline. The gender-age-physiology (GAP) index was calculated in each case.
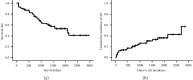
Results: The study population (59 men and 12 women) had a median age of 67 years. Serum anti-MX1 IgG and IgA autoantibody levels correlated positively with GAP stage (p < 0.05). Univariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis did not identify an elevated anti-MX1 IgG, IgA, or IgM autoantibody level as a significant prognostic factor; however, a higher anti-MX1 IgA autoantibody level heralded significantly poorer survival after adjustment for GAP stage (p=0.030) and for percent forced vital capacity and modified Medical Research Council score (p=0.018). Neither the anti-MX1 IgG autoantibody nor the IgM autoantibody could predict survival after these adjustments.
Conclusions: The serum anti-MX1 IgA autoantibody level is a significant prognostic factor in IPF. Further studies are needed to clarify the pathophysiological role of this autoantibody in IPF.
Copyright © 2022 Toru Arai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AM is an employee of Medical and Biological Laboratory Co., Ltd. (MBL). The study was performed in collaboration between the authors' institutions and MBL. YI is an advisor to Boehringer Ingelheim, Taiho, Roche, and SAVARA. YI has received lecture fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Shionogi, and GSK. TA has received lecture fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and Shionogi for activities not connected with the submitted work. MH, YH, TK, HK, and AK declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serum IgA levels and survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: association with serum cytokine levels and peripheral monocyte counts.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Apr 30;17(4):2038-2049. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2024-2142. Epub 2025 Apr 28. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40400959 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias using anti-myxovirus resistance-protein 1 autoantibody.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 23;7:43201. doi: 10.1038/srep43201. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28230086 Free PMC article.
-
Real-life experiences in a single center: efficacy of pirfenidone in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and fibrotic idiopathic non-specific interstitial pneumonia patients.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2020 Jan-Dec;14:1753466620963015. doi: 10.1177/1753466620963015. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2020. PMID: 33070705 Free PMC article.
-
Serum metalloproteinases 1 and 7 in the diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other interstitial pneumonias.Respir Med. 2015 Aug;109(8):1063-8. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Respir Med. 2015. PMID: 26174192
-
A cohort study of Danish patients with interstitial lung diseases: burden, severity, treatment and survival.Dan Med J. 2015 Apr;62(4):B5069. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25872544 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning-based integration identifies plasma cells-related gene signature ST6GAL1 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):295. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03696-9. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40604645 Free PMC article.
-
Serum surfactant protein D as a significant biomarker for predicting occurrence, progression, acute exacerbation, and mortality in interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 14;16:1450798. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1450798. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40028331 Free PMC article.
-
Recent updates of interferon-derived myxovirus resistance protein A as a biomarker for acute viral infection.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Dec 23;29(1):612. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02221-8. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39710743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum IgA levels and survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: association with serum cytokine levels and peripheral monocyte counts.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Apr 30;17(4):2038-2049. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2024-2142. Epub 2025 Apr 28. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40400959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raghu G., Collard H. R., Egan J. J., et al. On behalf of the ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Committee on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine . 2011;183:788–824. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

