The Effect of Inter-pulse Interval on TMS Motor Evoked Potentials in Active Muscles
- PMID: 35392119
- PMCID: PMC8980278
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.845476
The Effect of Inter-pulse Interval on TMS Motor Evoked Potentials in Active Muscles
Abstract
Objective: The time interval between transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) pulses affects evoked muscle responses when the targeted muscle is resting. This necessitates using sufficiently long inter-pulse intervals (IPIs). However, there is some evidence that the IPI has no effect on the responses evoked in active muscles. Thus, we tested whether voluntary contraction could remove the effect of the IPI on TMS motor evoked potentials (MEPs).
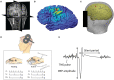
Methods: In our study, we delivered sets of 30 TMS pulses with three different IPIs (2, 5, and 10 s) to the left primary motor cortex. These measurements were performed with the resting and active right hand first dorsal interosseous muscle in healthy participants (N = 9 and N = 10). MEP amplitudes were recorded through electromyography.
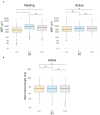
Results: We found that the IPI had no significant effect on the MEP amplitudes in the active muscle (p = 0.36), whereas in the resting muscle, the IPI significantly affected the MEP amplitudes (p < 0.001), decreasing the MEP amplitude of the 2 s IPI.
Conclusions: These results show that active muscle contraction removes the effect of the IPI on the MEP amplitude. Therefore, using active muscles in TMS motor mapping enables faster delivery of TMS pulses, reducing measurement time in novel TMS motor mapping studies.
Keywords: TMS; active muscle contraction; inter-pulse interval; motor evoked potential; motor mapping; motor threshold.
Copyright © 2022 Matilainen, Soldati and Laakso.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Çan M. K., Laakso I., Nieminen J. O., Murakami T., Ugawa Y. (2018). Coil model comparison for cerebellar transcranial magnetic stimulation. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Exp.. 5, 015020. 10.1088/2057-1976/aaee5b - DOI
-
- Chen R., Classen J., Gerloff C., Celnik P., Wassermann E., Hallett M., et al. . (1997). Depression of motor cortex excitability by low-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology 48, 1398–1403. - PubMed
-
- Dale A. M., Fischl B., Sereno M. I. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis: I. segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage 9, 179–194. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

