Normal Weight Obesity: Role of apoB and Insulin Sensitivity in Predicting Future Cardiovascular Risk
- PMID: 35392312
- PMCID: PMC8980834
- DOI: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_139_20
Normal Weight Obesity: Role of apoB and Insulin Sensitivity in Predicting Future Cardiovascular Risk
Abstract
Background: According to NFHS-4 survey, obesity has doubled in India. BMI cannot differentiate body fat from lean mass. Normal weight obesity was defined to distinguish people with normal BMI and increased body fat percentage (BF%). In contrast to conventional atherogenic prediction, Apolipoprotein B level is elevated before LDL cholesterol. Adiposity is also known for causing insulin resistance. Hence this study is an attempt to find the correlation of apo B and Insulin sensitivity in predicting future cardiovascular risk among normal weight obese. To study the role of apoB and insulin resistance in predicting cardio vascular risk.
Methods: 269 participants of age group 18-24 in a medical teaching institute were selected for the first phase of the study through systematic random sampling. BF% was calculated with Harpenden skinfold callipers using Jackson Pollock's method. Second phase of the study involved biochemical investigation of 30 NWO participants. ApoB level and insulin sensitivity using HOMA model was estimated. Spearman correlations and simple linear regression were used. Analysis done using SPSSv16.
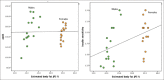
Results: Male and Females were 56.4% and 43.6%, respectively. Out of 269, 44 were found to be having NWO. Hence Prevalence was 16.4%.There is a positive correlation found between apoB and insulin resistance with increasing body fat percentage.
Conclusions: Elevated levels of apo B and insulin resistance are seen in NWO individuals as the BF% increases. NWO should be diagnosed early and thus apoB and insulin resistance can be screened for cardio vascular risk prediction.
Keywords: Adiposity; atherogenicity; body fat percentage; cardiovascular risk; diabetes; insulin sensitivity; lean mass.
Copyright: © 2022 International Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Family Health Survey - 4 2015
-
- Madeira FB, Published S, Veloso HF, Goldani MZ, Kac G, Cardoso VC, et al. Normal weight obesity is associated with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in young adults from a middle-income country normal weight obesity is associated with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in young adults from a middle-incom. PLoS One. 2013;8:1–10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barter PJ, Ballantyne CM, Carmena R, Cabezas MC, Chapman MJ, Couture P, et al. Apo B versus cholesterol in estimating cardiovascular risk and in guiding therapy: Report of the thirty-person/ten-country panel. J Intern Med. 2006;259:247–58. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous