Menstrual and Reproductive Factors and Risk of Breast Cancer in Iranian Female Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35392324
- PMCID: PMC8980831
- DOI: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_646_20
Menstrual and Reproductive Factors and Risk of Breast Cancer in Iranian Female Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer (BC) is the most frequent cancer in Iranian females. Due to the changes in lifestyle and reproductive risk factors, the BC incidence rate has been rapidly increasing. Knowing risk factors of BC could significantly contribute to improve preventive behaviors. To investigate the relationship between menstrual and reproductive factors and BC in Iranian female population.
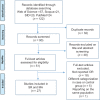
Methods: Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, and SID as well as references of included studies were searched. Among relevant published observational studies, 27 studies met the inclusion criteria. Pooled risk estimates for the risk factors were determined using random-effects models due to the presence of substantial heterogeneity (P < 0.05).
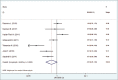
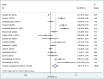
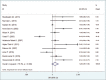
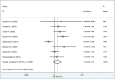
Results: All of the selected studies had case-control design. There was a positive relationship between maternal age at first pregnancy and risk of BC (OR = 1.79 95% CI: 1.36-2.35). Also, menopausal status was associated with higher risk of BC (OR = 1.60 95% CI: 1.18-2.17), whereas, there was no association between menarche age and increased risk of BC (OR = 0.55 95% CI: 0.29-1.03). History of abortion (OR = 1.21 95% CI: 0.97-1.5), nulliparity (OR = 1.43 95% CI: 0.89-2.31), and breastfeeding history (OR = 0.68 95% CI: 0.42-1.09) were not associated with BC risk.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that age at the first pregnancy and menopausal status were significantly associated with BC risk among Iranian women, whereas menarche age, nulliparity, and history of breastfeeding were not. In regard to the history of abortion, our findings revealed no association with BC, but in high-quality studies, this relationship was significant.
Keywords: Abortion (induced; breast neoplasm; breastfeeding; menopause; reproductive history; spontaneous).
Copyright: © 2022 International Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of reproductive risk factors and breast cancer molecular subtypes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jul 10;23(1):644. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11049-0. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37430191 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of reproductive factors on breast cancer incidence: Pooled analysis of nine cohort studies in Japan.Cancer Med. 2021 Mar;10(6):2153-2163. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3752. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33650323 Free PMC article.
-
Reproductive variables and risk of breast malignant and benign tumours in Yunnan province, China.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(5):2179-84. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2012.13.5.2179. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012. PMID: 22901191
-
Association of physical activity, body mass index and reproductive history with breast cancer by menopausal status in Iranian women.Cancer Epidemiol. 2020 Aug;67:101738. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2020.101738. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Cancer Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 32512496
-
Breast Cancer Risk From Modifiable and Non-Modifiable Risk Factors among Palestinian Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Jul 1;22(7):1987-1995. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.7.1987. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 34319018 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Adverse pregnancy outcomes and multiple cancers risk in both mother and offspring: an umbrella review of systematic reviews with meta-analyses of observational studies.BMC Med. 2024 Oct 11;22(1):454. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03680-w. BMC Med. 2024. PMID: 39394137 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for breast cancer: an umbrella review of observational cohort studies and causal relationship analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 May 2;15:1541233. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1541233. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40386557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Khakbazan Z, Taghipour A, Roudsari RL, Mohammadi E, Omranipour R. Delayed presentation of self-discovered breast cancer symptoms in Iranian women: A qualitative study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15:9427–32. - PubMed
-
- Karim SM, Baeshen W, Neamatullah SN, Bin B. Oral contraceptives, abortion and breast cancer risk: A case control study in Saudi Arabia. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16:3957–60. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
