RGMQL: scalable and interoperable computing of heterogeneous omics big data and metadata in R/Bioconductor
- PMID: 35392801
- PMCID: PMC8991469
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-022-04648-4
RGMQL: scalable and interoperable computing of heterogeneous omics big data and metadata in R/Bioconductor
Abstract
Background: Heterogeneous omics data, increasingly collected through high-throughput technologies, can contain hidden answers to very important and still unsolved biomedical questions. Their integration and processing are crucial mostly for tertiary analysis of Next Generation Sequencing data, although suitable big data strategies still address mainly primary and secondary analysis. Hence, there is a pressing need for algorithms specifically designed to explore big omics datasets, capable of ensuring scalability and interoperability, possibly relying on high-performance computing infrastructures.
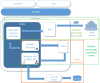
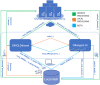
Results: We propose RGMQL, a R/Bioconductor package conceived to provide a set of specialized functions to extract, combine, process and compare omics datasets and their metadata from different and differently localized sources. RGMQL is built over the GenoMetric Query Language (GMQL) data management and computational engine, and can leverage its open curated repository as well as its cloud-based resources, with the possibility of outsourcing computational tasks to GMQL remote services. Furthermore, it overcomes the limits of the GMQL declarative syntax, by guaranteeing a procedural approach in dealing with omics data within the R/Bioconductor environment. But mostly, it provides full interoperability with other packages of the R/Bioconductor framework and extensibility over the most used genomic data structures and processing functions.
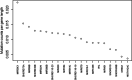
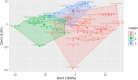
Conclusions: RGMQL is able to combine the query expressiveness and computational efficiency of GMQL with a complete processing flow in the R environment, being a fully integrated extension of the R/Bioconductor framework. Here we provide three fully reproducible example use cases of biological relevance that are particularly explanatory of its flexibility of use and interoperability with other R/Bioconductor packages. They show how RGMQL can easily scale up from local to parallel and cloud computing while it combines and analyzes heterogeneous omics data from local or remote datasets, both public and private, in a completely transparent way to the user.
Keywords: Data scalability; Distribution transparency; Heterogeneous omics big data; Tertiary data analysis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

