Outcomes following balloon tibioplasty versus conventional osteosynthesis techniques for Schatzker type III tibial plateau fractures: a systematic review
- PMID: 35392956
- PMCID: PMC8991579
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-022-02973-1
Outcomes following balloon tibioplasty versus conventional osteosynthesis techniques for Schatzker type III tibial plateau fractures: a systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Schatzker type III fractures of the tibial plateau require elevation of the depressed portions to regain articular congruity. Balloon tibioplasty has been used as an alternative to conventional metal instruments for elevation of the lateral tibial plateau. This study compared functional outcomes following balloon tibioplasty or conventional osteosynthesis techniques in patients with type III fractures of the tibial plateau.
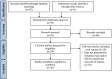
Materials and methods: A systematic literature search was performed using PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library to identify studies published through March 29, 2021, pertaining to balloon tibioplasty or conventional osteosynthesis techniques for type III fractures. Non-human studies, opinion or editorial pieces, systematic reviews, case series (< 5 patients), and articles published in a non-English language were excluded. Primary outcomes were Rasmussen clinical score, range of motion, and Knee Society Score (KSS). A Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) risk of bias assessment was performed for all studies.
Results: A total of 95 studies were identified, with 10 studies (and 132 total patients) meeting inclusion criteria: 1 study focused on balloon tibioplasty, 8 studies reported outcomes following conventional osteosynthesis, and 1 study compared outcomes of the two techniques. Mean follow-up times varied widely, from 4 to 76.3 months. Where reported, balloon tibioplasty resulted in good to excellent functional outcomes as indicated by Rasmussen clinical scores (mean 28.3 in a case series; mean 28.9 in a randomized controlled trial) and range of motion (≥ 140° in both studies) 1-2 years following surgery. KSS was not reported consistently enough for comparison. Studies ranged from low to high risk of bias according to the JBI assessment.
Conclusions: Balloon tibioplasty can lead to excellent functional outcomes in patients with depression fractures of the lateral tibial plateau. More research is needed to directly compare outcomes following treatment with balloon tibioplasty or conventional osteosynthesis techniques.
Keywords: Articular range of motion; Balloon tibioplasty; Internal fracture fixation; Schatzker; Tibia; Tibial plateau.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional Outcomes of Bicolumnar Plating in Schatzker Type V and VI Proximal Tibial Fractures: A Prospective Study.Cureus. 2025 Jun 19;17(6):e86399. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86399. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40688965 Free PMC article.
-
[Osteotomy of non-core weight-bearing area of the lateral tibial plateau, reduction, and internal fixation in treatment of tibial plateau fractures involving posterolateral column collapse].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Apr 15;37(4):410-416. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202301019. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37070306 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Outcomes of arthroscopic-assisted lateral tibial plateau fixation: a systematic review.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023 Jul;33(5):1473-1483. doi: 10.1007/s00590-022-03339-3. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023. PMID: 35867167
-
[Short-term effectiveness of minimally invasive treatment for posterolateral depressed tibial plateau fractures assisted by robots and arthroscopy].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Jul 15;39(7):801-806. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202505004. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40659581 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Clinical and radiological outcomes following arthroscopic-assisted management of tibial plateau fractures: a systematic review.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015 Dec;23(12):3464-72. doi: 10.1007/s00167-014-3256-2. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015. PMID: 25246171 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Arthroscopic bone grafting for Schatzker III tibial plateau fractures: a retrospective comparative study.Sci Rep. 2025 May 16;15(1):17081. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99644-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40379915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schatzker J, McBroom R, Bruce D. The tibial plateau fracture. The Toronto experience 1968–1975. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979;138:94–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

