Cancer combination therapies by angiogenesis inhibitors; a comprehensive review
- PMID: 35392964
- PMCID: PMC8991477
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-022-00838-y
Cancer combination therapies by angiogenesis inhibitors; a comprehensive review
Abstract
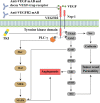
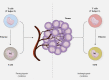
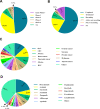
Abnormal vasculature is one of the most conspicuous traits of tumor tissue, largely contributing to tumor immune evasion. The deregulation mainly arises from the potentiated pro-angiogenic factors secretion and can also target immune cells' biological events, such as migration and activation. Owing to this fact, angiogenesis blockade therapy was established to fight cancer by eliminating the nutrient and oxygen supply to the malignant cells by impairing the vascular network. Given the dominant role of vascular-endothelium growth factor (VEGF) in the angiogenesis process, the well-known anti-angiogenic agents mainly depend on the targeting of its actions. However, cancer cells mainly show resistance to anti-angiogenic agents by several mechanisms, and also potentiated local invasiveness and also distant metastasis have been observed following their administration. Herein, we will focus on clinical developments of angiogenesis blockade therapy, more particular, in combination with other conventional treatments, such as immunotherapy, chemoradiotherapy, targeted therapy, and also cancer vaccines. Video abstract.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Anti-angiogenic agents; Combination therapy; Resistance; Tumor.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There is no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

