Development and preliminary validation of the Sjögren's Tool for Assessing Response (STAR): a consensual composite score for assessing treatment effect in primary Sjögren's syndrome
- PMID: 35393271
- PMCID: PMC9209686
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-222054
Development and preliminary validation of the Sjögren's Tool for Assessing Response (STAR): a consensual composite score for assessing treatment effect in primary Sjögren's syndrome
Abstract
Objective: To develop a composite responder index in primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS): the Sjögren's Tool for Assessing Response (STAR).
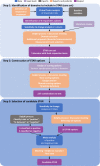
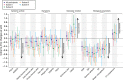
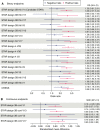
Methods: To develop STAR, the NECESSITY (New clinical endpoints in primary Sjögren's syndrome: an interventional trial based on stratifying patients) consortium used data-driven methods based on nine randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and consensus techniques involving 78 experts and 20 patients. Based on reanalysis of rituximab trials and the literature, the Delphi panel identified a core set of domains with their respective outcome measures. STAR options combining these domains were proposed to the panel for selection and improvement. For each STAR option, sensitivity to change was estimated by the C-index in nine RCTs. Delphi rounds were run for selecting STAR. For the options remaining before the final vote, a meta-analysis of the RCTs was performed.
Results: The Delphi panel identified five core domains (systemic activity, patient symptoms, lachrymal gland function, salivary gland function and biological parameters), and 227 STAR options combining these domains were selected to be tested for sensitivity to change. After two Delphi rounds, a meta-analysis of the 20 remaining options was performed. The candidate STAR was then selected by a final vote based on metrological properties and clinical relevance.
Conclusion: The candidate STAR is a composite responder index that includes all main disease features in a single tool and is designed for use as a primary endpoint in pSS RCTs. The rigorous and consensual development process ensures its face and content validity. The candidate STAR showed good sensitivity to change and will be prospectively validated by the NECESSITY consortium in a dedicated RCT.
Keywords: Sjogren's syndrome; outcome assessment, health care; patient reported outcome measures.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RS has received consulting fees from GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer, Janssen and Novartis, participated in an advisory board for Janssen, and received support for attending meeting from GlaxoSmithKline and Amgen. DC has received consulting fees from GlaxoSmithKline, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Amgen, Pfizer and Roche. J-EG has received honoraria from AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Novartis, MSD, CSL Behring and Genzyme and received grant from Bristol Myers Squibb. SJB and BF receive funding from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Birmingham Biomedical Research Centre, Birmingham, UK. SJB has provided consultancy services in the field of clinical trial design for Sjögren’s syndrome for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Galapagos and Novartis Pharmaceuticals in 2018–2021. BF has received grants from Servier, Galapagos and Janssen, provided consultancy services for Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen and Servier, and received honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb and Novartis. MB has received grants from Amgen/MedImmune, Janssen and GlaxoSmithKline, and personal fees from UCB, Amgen/MedImmune, Janssen and GlaxoSmithKline. HB has received grants from Bristol Myers Squibb and Roche, and consulting fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche, Novartis, MedImmune and Union Chimique Belge. WH and PG are employees of Novartis Pharma and recipients of Novartis stocks. XM has received a grant from Ose Pharmaceuticals and consultancy fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB. GB, MC, EP, JAvR, VD-P and RP declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

