Innovative, centralised, multidisciplinary medicines optimisation clinic for PCSK9 inhibitors
- PMID: 35393352
- PMCID: PMC8991064
- DOI: 10.1136/openhrt-2021-001931
Innovative, centralised, multidisciplinary medicines optimisation clinic for PCSK9 inhibitors
Abstract
Background: Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors (PCSK9is) are an important but underutilised option to help optimise lipid management. We developed a new service to improve patient access to these medicines in line with National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommendations. This paper describes the model and provides lipid-lowering results and feedback from the first 100 referred patients.
Methods: The service is based on a centralised multidisciplinary clinic that is the sole prescriber of PCSK9i therapy in the area. Referred patients are assessed for eligibility and given tailored, person-centred support, education and monitoring to promote treatment adherence and lipids optimisation. The clinic also supports referred patients that do not meet PCSK9i eligibility criteria.
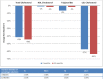
Results: Among the first 100 patients referred (n=62 male; mean age: 62.9±10.5 years), 48 were initiated on PCSK9i therapy. Mean total cholesterol decreased from 7.7±1.6 mmol/L at baseline to 4.5±1.4 mmol/L at 3 months (41% reduction), while mean low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) fell from 5.0±1.6 mmol/L to 2.1±1.3 mmol/L (58% reduction; p<0.0001) and median LDL-C decreased from 4.8 mmol/L to 1.6 mmol/L (67% reduction) over the same period. These decreases were maintained at 12 months (45%, 65% and 67% reductions, respectively; p<0.0001 for the decrease in mean LDL-C from baseline). Patient feedback on the clinic was positive and overall satisfaction was high.
Conclusions: This innovative, person-centred, multidisciplinary service successfully initiated PCSK9i therapy for eligible patients and drove long-term monitoring, adherence and cholesterol lowering. It also provided medicines optimisation and adherence assistance to PCSK9i-ineligible patients. The model could be used in other areas to support better uptake and optimisation of PCSK9i therapy.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Delivery of Health Care; Hyperlipidemias.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Nothing to declare. RK received speaker fees from Sanofi.
Figures

References
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Clinical guideline [CG181]. Cardiovascular disease: risk assessment and reduction, including lipid modification, 2016. Available: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg181 [Accessed 26 Oct 2021]. - PubMed
-
- Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL. ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J 2019;2020:111–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
