Shapes of subcortical structures in adolescents with and without familial history of substance use disorder
- PMID: 35393707
- PMCID: PMC9120549
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.25804
Shapes of subcortical structures in adolescents with and without familial history of substance use disorder
Abstract
It has been suggested that intergenerational transmission of risk for substance use disorder (SUD) manifests in the brain anatomy of substance naïve adolescents. While volume and shapes of subcortical structures (SSS) have been shown to be heritable, these structures, especially the pallidum, putamen, nucleus accumbens, and hippocampus, have also been associated with substance use disorders. However, it is not clear if those anatomical differences precede substance use or are the result of that use. Therefore, we examined if volume and SSS of adolescents with a family history (FH+) of SUD differed from adolescents without such a history (FH-). Because risk for SUD is associated with anxiety and impulsivity, we also examined correlations between these psychological characteristics and volume/SSS. Using structural MRI and FSL software, we segmented subcortical structures and obtained indices of SSS and volumes of 64 FH+ and 58 FH- adolescents. We examined group differences in volume and SSS, and the correlations between volume/SSS and trait anxiety and impulsivity. FH+ adolescents had a significant inward deformation in the shape of the right anterior hippocampus compared to FH- adolescents, while the volume of this structure did not differ between groups. Neither shape nor volume of the other subcortical structures differed between groups. In the FH+ adolescents, the left hippocampus shape was positively correlated with both trait anxiety and impulsivity, while in FH- adolescents a negative correlation pattern of SSS was seen in the hippocampus. SSS appears to capture local anatomical features that traditional volumetric analysis does not. The inward shape deformation in the right anterior hippocampus in FH+ adolescents may be related to the known increased risk for behavioral dysregulation leading to SUD in FH+ offspring. Hippocampus shape also exhibits opposite patterns of correlation with anxiety and impulsivity scores across the FH+ and FH- adolescents. These novel findings may reveal neural correlates, not captured by traditional volumetric analysis, of familial transmission of increased vulnerability to SUD.
Keywords: MRI; adolescents; familial risk for SUD; shape analysis; subcortical brain structures; substance use disorder (SUD).
© 2022 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors report any financial relationships with commercial interests.
Figures
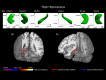


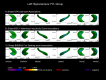
Similar articles
-
Effects of substance misuse and current family history of substance use disorder on brain structure in adolescents and young adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021 Nov 1;228:109032. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2021.109032. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021. PMID: 34555690
-
White matter integrity and functional connectivity in adolescents with a parental history of substance use disorder.Neuroimage Rep. 2021 Sep;1(3):100037. doi: 10.1016/j.ynirp.2021.100037. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Neuroimage Rep. 2021. PMID: 36320407 Free PMC article.
-
Cingulate Cortex Structural Alterations in Substance Use Disorder Psychiatric Inpatients.Am J Addict. 2021 Jan;30(1):72-79. doi: 10.1111/ajad.13093. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Am J Addict. 2021. PMID: 33232571
-
Impulsivity traits and neurocognitive mechanisms conferring vulnerability to substance use disorders.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Feb 1;183:108402. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108402. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33189766 Review.
-
The neurobiology of impulsivity and substance use disorders: implications for treatment.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019 Sep;1451(1):71-91. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13977. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019. PMID: 30291624 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of chemotherapy on hippocampal volume and shape in older long-term breast cancer survivors.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Mar 8;16:1347721. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1347721. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38524113 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal quantitative magnetic resonance imaging alterations of the basal ganglia circuit underlie the severity of bulimia nervosa.Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2025 Jan-Mar;25(1):100557. doi: 10.1016/j.ijchp.2025.100557. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40161006 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in stress responses among underrepresented minority adolescents at risk for substance use disorder.Int J Psychophysiol. 2023 Sep;191:42-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2023.07.003. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Int J Psychophysiol. 2023. PMID: 37517602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdallah, C. G. , Coplan, J. D. , Jackowski, A. , Sato, J. R. , Mao, X. , Shungu, D. C. , & Mathew, S. J. (2013). A pilot study of hippocampal volume and N‐acetylaspartate (NAA) as response biomarkers in riluzole‐treated patients with GAD. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 23(4), 276–284. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker, B. H. , Lugo‐Candelas, C. , Wu, H. , Laue, H. E. , Boivin, A. , Gillet, V. , … Baccarelli, A. A. (2020). Association of prenatal acetaminophen exposure measured in meconium with risk of attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder mediated by frontoparietal network brain connectivity. JAMA Pediatrics, 174(11), 1073–1081. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bloomer, C. W. , Langleben, D. D. , & Meyerhoff, D. J. (2004). Magnetic resonance detects brainstem changes in chronic, active heavy drinkers. Psychiatry Research, 132(3), 209–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

