Fermentation of plant-based dairy alternatives by lactic acid bacteria
- PMID: 35393728
- PMCID: PMC9049613
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.14008
Fermentation of plant-based dairy alternatives by lactic acid bacteria
Abstract
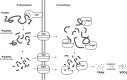
Ethical, environmental and health concerns around dairy products are driving a fast-growing industry for plant-based dairy alternatives, but undesirable flavours and textures in available products are limiting their uptake into the mainstream. The molecular processes initiated during fermentation by lactic acid bacteria in dairy products is well understood, such as proteolysis of caseins into peptides and amino acids, and the utilisation of carbohydrates to form lactic acid and exopolysaccharides. These processes are fundamental to developing the flavour and texture of fermented dairy products like cheese and yoghurt, yet how these processes work in plant-based alternatives is poorly understood. With this knowledge, bespoke fermentative processes could be engineered for specific food qualities in plant-based foods. This review will provide an overview of recent research that reveals how fermentation occurs in plant-based milk, with a focus on how differences in plant proteins and carbohydrate structure affect how they undergo the fermentation process. The practical aspects of how this knowledge has been used to develop plant-based cheeses and yoghurts is also discussed.
© 2022 The New Zealand Institute for Plant and Food Research Limited. Microbial Biotechnology published by Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abarquero, D. , Renes, E. , Fresno, J.M. , and Tornadijo, M.E. (2021) Study of exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria and their industrial applications: a review. Int J Food Sci Technol 57: 16–26. doi:10.1111/ijfs.15227. - DOI
-
- Adejuyitan, J.A. , Olanipekun, B.F. , and Moyinwin, O.A. (2014) Production and evaluation of cheese‐like product from the blend of soy milk and coconut milk. Arch Appl Sci Res 6: 263–266.
-
- Adeyemo, S.M. , and Onilude, A.A. (2013) Enzymatic reduction of anti‐nutritional factors in fermenting soybeans by Lactobacillus plantarum isolates from fermenting cereals. Niger Food J 31: 84–90.
-
- Aguirre, L. , Garro, M.S. , and Savoy de Giori, G. (2008) Enzymatic hydrolysis of soybean protein using lactic acid bacteria. Food Chem 111: 976–982.
-
- Aguirre, L. , Hebert, E.M. , Garro, M.S. , and Savoy de Giori, G. (2014) Proteolytic activity of Lactobacillus strains on soybean proteins. LWT ‐ Food Sci Technol 59: 780–785.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

