Agl24 is an ancient archaeal homolog of the eukaryotic N-glycan chitobiose synthesis enzymes
- PMID: 35394422
- PMCID: PMC8993221
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.67448
Agl24 is an ancient archaeal homolog of the eukaryotic N-glycan chitobiose synthesis enzymes
Abstract
Protein N-glycosylation is a post-translational modification found in organisms of all domains of life. The crenarchaeal N-glycosylation begins with the synthesis of a lipid-linked chitobiose core structure, identical to that in Eukaryotes, although the enzyme catalyzing this reaction remains unknown. Here, we report the identification of a thermostable archaeal β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase, named
Keywords: Agl24; Alg13; Alg14; E. coli; N-glycosylation; Sulfolobus acidocladarius; biochemistry; chemical biology; chitobiose; infectious disease; microbiology.
© 2022, Meyer et al.
Conflict of interest statement
BM, PA, BW, GK, AP, SA, HD No competing interests declared
Figures








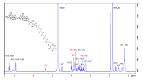

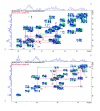







Similar articles
-
The multiple evolutionary origins of the eukaryotic N-glycosylation pathway.Biol Direct. 2016 Aug 4;11:36. doi: 10.1186/s13062-016-0137-2. Biol Direct. 2016. PMID: 27492357 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane topology of the Alg14 endoplasmic reticulum UDP-GlcNAc transferase subunit.J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 5;282(40):29081-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704410200. Epub 2007 Aug 8. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17686769
-
Production of initial-stage eukaryotic N-glycan and its protein glycosylation in Escherichia coli.J Biosci Bioeng. 2015 Apr;119(4):399-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2014.09.016. Epub 2014 Oct 16. J Biosci Bioeng. 2015. PMID: 25449758
-
N-glycosylation in Archaea-New roles for an ancient posttranslational modification.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Nov;114(5):735-741. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14569. Epub 2020 Jul 26. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32633872 Review.
-
N-linked glycosylation in Archaea: a structural, functional, and genetic analysis.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2014 Jun;78(2):304-41. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00052-13. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24847024 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An in vitro assay for enzymatic studies on human ALG13/14 heterodimeric UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 19;10:1008078. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1008078. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36200043 Free PMC article.
-
ALG13-Congenital Disorder of Glycosylation (ALG13-CDG): Updated clinical and molecular review and clinical management guidelines.Mol Genet Metab. 2024 Jun;142(2):108472. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2024.108472. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Mol Genet Metab. 2024. PMID: 38703411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-glycosylation in Archaea - Expanding the process, components and roles of a universal post-translational modification.BBA Adv. 2024 Aug 29;6:100120. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2024.100120. eCollection 2024. BBA Adv. 2024. PMID: 39296579 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of carbohydrates and glycoconjugates by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: An update for 2021-2022.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2025 May-Jun;44(3):213-453. doi: 10.1002/mas.21873. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2025. PMID: 38925550 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abu-Qarn M, Yurist-Doutsch S, Giordano A, Trauner A, Morris HR, Hitchen P, Medalia O, Dell A, Eichler J. Haloferax volcanii AglB and AglD are involved in N-glycosylation of the S-layer glycoprotein and proper assembly of the surface layer. Journal of Molecular Biology. 2007;374:1224–1236. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.10.042. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

