Prefrontal cortical activation in Internet Gaming Disorder Scale high scorers during actual real-time internet gaming: A preliminary study using fNIRS
- PMID: 35394923
- PMCID: PMC9295239
- DOI: 10.1556/2006.2022.00017
Prefrontal cortical activation in Internet Gaming Disorder Scale high scorers during actual real-time internet gaming: A preliminary study using fNIRS
Abstract
Background: Observation of real-time neural characteristics during gameplay would provide distinct evidence for discriminating the currently controversial diagnosis of internet gaming disorder (IGD), and elucidate neural mechanisms that may be involved in addiction. We aimed to provide preliminary findings on possible neural features of IGD during real-time internet gaming using functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS).
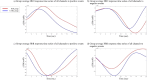
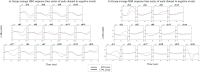
Methods: Prefrontal cortical activations accompanying positive and negative in-game events were investigated. Positive events: (1) participant's champion slays or assists in slaying an opponent without being slain. (2) the opposing team's nexus is destroyed. Negative events: (1) participant's champion is slain without slaying or assisting in slaying any opponent. (2) the team's nexus is destroyed. Collected data were compared between the IGD group and control group, each with 15 participants.
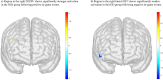
Results: The IGD group scored significantly higher than the CTRL group on the craving scale. Following positive events, the IGD group displayed significantly stronger activation in the DLPFC. Following negative events, the IGD group displayed significantly weaker activation in the lateral OFC.
Discussion and conclusions: Individuals scoring high on the IGD scale may crave for more internet gaming after encountering desired events during the game. Such observations are supported by the correlation between the craving scale and DLPFC activation. The IGD group may also show diminished punishment sensitivity to negative in-game experiences rendering them to continue playing the game. The present study provides preliminary evidence that IGD may demonstrate neural characteristics observed in other addictive disorders and suggests the use of fNIRS in behavioral addiction studies.
Keywords: addiction; dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; fNIRS; internet gaming disorder; orbitofrontal cortex; real-time internet gaming.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


 .
.
 .
.

Similar articles
-
Prefrontal cortex responses to game rewards and losses in individuals with Internet Gaming Disorder: Insights from fNIRS during mobile gameplay.J Behav Addict. 2025 Jan 21;14(1):347-360. doi: 10.1556/2006.2024.00076. Print 2025 Mar 28. J Behav Addict. 2025. PMID: 39841152 Free PMC article.
-
Brain responses to positive and negative events in individuals with internet gaming disorder during real gaming.J Behav Addict. 2023 Aug 30;12(3):758-774. doi: 10.1556/2006.2023.00039. Print 2023 Oct 5. J Behav Addict. 2023. PMID: 37651282 Free PMC article.
-
Gender-related differences in cue-elicited cravings in Internet gaming disorder: The effects of deprivation.J Behav Addict. 2018 Dec 1;7(4):953-964. doi: 10.1556/2006.7.2018.118. Epub 2018 Dec 17. J Behav Addict. 2018. PMID: 30556781 Free PMC article.
-
Internet Gaming Disorder: An Emergent Health Issue for Men.Am J Mens Health. 2018 Jul;12(4):1151-1159. doi: 10.1177/1557988318766950. Epub 2018 Apr 1. Am J Mens Health. 2018. PMID: 29606034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers of Internet Gaming Disorder-A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 28;13(17):5110. doi: 10.3390/jcm13175110. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39274323 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Dark Side of Leisure Time: Analysis of the Predictive Effects Between Boredom, Internet Usage Habits, and Gambling Behaviors.Brain Sci. 2025 Jun 3;15(6):598. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15060598. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40563770 Free PMC article.
-
Increasingly dependent on habit? A study on the electrophysiological mechanisms of goal-directed and habitual control in internet gaming disorder.J Behav Addict. 2025 May 15;14(2):757-775. doi: 10.1556/2006.2024.00084. Print 2025 Jul 2. J Behav Addict. 2025. PMID: 40372798 Free PMC article.
-
Prefrontal cortex responses to game rewards and losses in individuals with Internet Gaming Disorder: Insights from fNIRS during mobile gameplay.J Behav Addict. 2025 Jan 21;14(1):347-360. doi: 10.1556/2006.2024.00076. Print 2025 Mar 28. J Behav Addict. 2025. PMID: 39841152 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Influence of Dual-Task Activities on Prefrontal Activation and Gait Variables in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment during Straight and Curved Walking.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jan 29;60(2):235. doi: 10.3390/medicina60020235. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38399523 Free PMC article.
-
Prefrontal Cortex Activation during Memory Training by Virtual Drum Beating: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Sep 15;11(18):2559. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11182559. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37761756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Substance-related and addictive disorders. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596.dsm16. - DOI
-
- Bak, S. , Jeong, J. , & Shin, J. (2021). Mutual interaction between genders with stress or non-stress by positive stimulus characteristics using fNIRS. 9th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) , 1–5. 10.1109/BCI51272.2021.9385362. - DOI
-
- Billieux, J. , Deleuze, J. , Griffiths, M. D. , & Kuss, D. J. (2015). Internet gaming addiction: The case of massively multiplayer online role-playing games. Textbook of Addiction Treatment: International Perspectives , 1515–1525.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

