Multimarker synaptic protein cerebrospinal fluid panels reflect TDP-43 pathology and cognitive performance in a pathological cohort of frontotemporal lobar degeneration
- PMID: 35395770
- PMCID: PMC8991834
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-022-00534-y
Multimarker synaptic protein cerebrospinal fluid panels reflect TDP-43 pathology and cognitive performance in a pathological cohort of frontotemporal lobar degeneration
Abstract
Background: Synapse degeneration is an early event in pathological frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD). Consequently, a surrogate marker of synapse loss could be used to monitor early pathologic changes in patients with underlying FTLD. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship of antemortem cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of 8 synaptic proteins with postmortem global tau and TDP-43 burden and cognitive performance and to assess their diagnostic capacity in a neuropathological FTLD cohort.
Methods: We included patients with a neuropathological confirmation of FTLD-Tau (n = 24, mean age-at-CSF 67 years ± 11), FTLD-TDP (n = 25, 66 years ± 9) or AD (n = 25, 73 years ± 6) as well as cognitively normal controls (n = 35, 69 years ± 7) from the Penn FTD Center and ADRC. We used a semi-quantitative measure of tau and TDP-43 inclusions to quantify pathological burden across 16 brain regions. Statistical methods included Spearman rank correlations, one-way analysis of covariance, ordinal regression, step-wise multiple linear regression and receiver-operating characteristic curves.
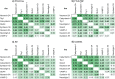
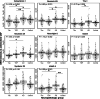
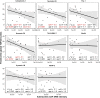
Result: CSF calsyntenin-1 and neurexin-2a were correlated in all patient groups (rs = .55 to .88). In FTLD-TDP, we observed low antemortem CSF levels of calsyntenin-1 and neurexin-2a compared to AD (.72-fold, p = .001, .77-fold, p = .04, respectively) and controls (.80-fold, p = .02, .78-fold, p = .02, respectively), which were inversely associated with post-mortem global TDP-43 burden (regression r2 = .56, p = .007 and r2 = .57, p = .006, respectively). A multimarker panel including calsyntenin-1 was associated with TDP-43 burden (r2 = .69, p = .003) and MMSE score (r2 = .19, p = .03) in FTLD. A second multimarker synaptic panel, also including calsyntenin-1, was associated with MMSE score in FTLD-tau (r2 = .49, p = .04) and improved diagnostic performance to discriminate FTLD-Tau and FTLD-TDP neuropathologic subtypes (AUC = .83).
Conclusion: These synaptic panels have potential in the differential diagnosis of FTLD neuropathologic subtypes and as surrogate markers of cognitive performance in future clinical trials targeting TDP-43 or tau.
Keywords: Biomarker; Calsyntenin-1; Cerebrospinal fluid; Frontotemporal dementia; Frontotemporal lobar degeneration; TDP-43; Tau.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
OB, AL, JF and DA declare a filed patent application (pending) to the European Patent Office for Markers of synaptopathy neurodegenerative disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduced CSF p-Tau181 to Tau ratio is a biomarker for FTLD-TDP.Neurology. 2013 Nov 26;81(22):1945-52. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000436625.63650.27. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Neurology. 2013. PMID: 24174584 Free PMC article.
-
LATE-NC Stage 3: a diagnostic rubric to differentiate severe LATE-NC from FTLD-TDP.Acta Neuropathol. 2025 Apr 28;149(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s00401-025-02876-5. Acta Neuropathol. 2025. PMID: 40293530 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG) in Cerebrospinal Fluid Does Not Discriminate between the Main FTLD Pathological Subtypes but Correlates with Cognitive Decline in FTLD Tauopathies.Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 8;11(10):1484. doi: 10.3390/biom11101484. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34680117 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers for the Differential Diagnosis between Alzheimer's Disease and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: Systematic Review, HSROC Analysis, and Confounding Factors.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;55(2):625-644. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160366. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 27716663
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The use of synaptic biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid to differentiate behavioral variant of frontotemporal dementia from primary psychiatric disorders and Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Feb 14;16(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01409-8. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38355535 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 and glial fibrillary acidic protein associate with synaptic density in older adults without dementia.Brain Commun. 2025 May 27;7(4):fcaf207. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcaf207. eCollection 2025. Brain Commun. 2025. PMID: 40620474 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic biomarkers in the cerebrospinal fluid associate differentially with classical neuronal biomarkers in patients with Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023 Mar 24;15(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01212-x. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 36964594 Free PMC article.
-
TDP-43 CSF Concentrations Increase Exponentially with Age in Metropolitan Mexico City Young Urbanites Highly Exposed to PM2.5 and Ultrafine Particles and Historically Showing Alzheimer and Parkinson's Hallmarks. Brain TDP-43 Pathology in MMC Residents Is Associated with High Cisternal CSF TDP-43 Concentrations.Toxics. 2022 Sep 24;10(10):559. doi: 10.3390/toxics10100559. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36287840 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling New Genetic Variants Associated with Age at Onset in Alzheimer's Disease and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration Due to C9orf72 Repeat Expansions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 7;25(13):7457. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137457. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henstridge CM, Sideris DI, Carroll E, Rotariu S, Salomonsson S, Tzioras M, McKenzie CA, Smith C, von Arnim CAF, Ludolph AC, et al. Synapse loss in the prefrontal cortex is associated with cognitive decline in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2018;135:213–226. doi: 10.1007/s00401-017-1797-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lleo A, Nunez-Llaves R, Alcolea D, Chiva C, Balateu-Panos D, Colom-Cadena M, Gomez-Giro G, Munoz L, Querol-Vilaseca M, Pegueroles J, et al. Changes in synaptic proteins precede neurodegeneration markers in preclinical Alzheimer's disease cerebrospinal fluid. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019;18:546–560. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.001290. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

