Evaluation of right ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunctions in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with poor glycemic control by layer specific global longitudinal strain and strain rate
- PMID: 35395870
- PMCID: PMC8994348
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-022-00820-1
Evaluation of right ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunctions in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with poor glycemic control by layer specific global longitudinal strain and strain rate
Abstract
Background: In order to evaluate right ventricular (RV) systolic and diastolic dysfunctions in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with poor glycemic control by layer specific global longitudinal strain (GLS) and strain rate (GLSr).
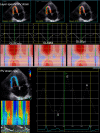
Methods: 68 T2DM patients and 66 normal controls were enrolled for the present study. RV layer specific GLS (GLSEpi, GLSMid and GLSEndo represent the epimyocardial, middle layer and endomyocardial strains, respectively) and GLSr (GLSr-S, GLSr-E and GLSr-A represent the systole, early-diastole and late-diastole strain rate) were calculated by averaging each of the three regional peak systolic strains and strain rates along the entire RV free-wall (RVFW), entire RV free-wall and septal wall (RVFSW) on RV-focused view.
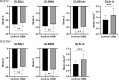
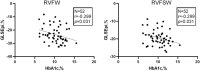
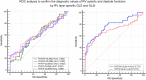
Results: The absolute values of RV layer specific GLS (GLSEpi, GLSMid and GLSEndo) in RVFW in T2DM patients were significantly lower than normal controls (P < 0.01), while GLSr-A was significantly larger than normal controls (P < 0.001). The absolute values of RV layer specific GLS (GLSEpi and GLSMid) in RVFSW in T2DM patients were significantly lower than normal controls (P < 0.05), while GLSr-A was significantly larger than normal controls (P < 0.001). HbA1c were poor negatived correlated with GLSEpi in RVFW and RVFSW in T2DM patients (P < 0.05). ROC analysis showed that RV layer specific GLS and GLSr-A had a high diagnostic efficacy in T2DM patients, and GLSr-A in RVFSW have the best diagnostic value in RV diastolic function in T2DM patients (AUC: 0.773).
Conclusion: From the research, we found that layer specific GLS and GLSr could detect the RV myocardial dysfunctions and confirmed that the impaired RV systolic and diastole functions in T2DM patients with poor glycemic control. GLSr-A in RVFSW had the best diagnostic value in evaluating RV diastolic function in T2DM patients.
Keywords: Diastole; Dysfunction; Right ventricle; Systolic; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of left ventricular systolic function in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with and without peripheral vascular disease.World J Diabetes. 2024 Jun 15;15(6):1280-1290. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1280. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38983825 Free PMC article.
-
Subclinical impairment of left ventricular myocardium function in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with or without hypertension.World J Diabetes. 2024 Jun 15;15(6):1272-1279. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1272. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38983828 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of right ventricular global longitudinal function in patients with tetralogy of fallot by two-dimensional ultrasound speckle tracking imaging.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2010 Feb;30(1):126-31. doi: 10.1007/s11596-010-0123-3. Epub 2010 Feb 14. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 20155469
-
Right ventricular free wall longitudinal strain and strain rate quantification with cardiovascular magnetic resonance based tissue tracking.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Oct;36(10):1985-1996. doi: 10.1007/s10554-020-01895-5. Epub 2020 May 27. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32462446 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of subclinical left ventricular systolic dysfunction in patients with acute-phase Kawasaki disease by hematological indices, layer-specific left ventricular longitudinal strain and global myocardial work.J Clin Ultrasound. 2023 Jun;51(5):764-773. doi: 10.1002/jcu.23442. Epub 2023 Feb 11. J Clin Ultrasound. 2023. PMID: 36773287
Cited by
-
The right ventricular dysfunction and ventricular interdependence in patients with DM: assessment using cardiac MR feature tracking.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Apr 21;22(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01806-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37085847 Free PMC article.
-
Diastolic global longitudinal strain and acute ischemic stroke: a hidden relationship?BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 May 19;25(1):383. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04841-2. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40389876 Free PMC article.
-
Association between subclinical right ventricular alterations and aerobic exercise capacity in type 2 diabetes.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2024 Winter;26(2):101120. doi: 10.1016/j.jocmr.2024.101120. Epub 2024 Oct 28. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2024. PMID: 39477154 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia Are Associated with In-Hospital Mortality among Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Supported with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation.J Clin Med. 2022 Aug 30;11(17):5106. doi: 10.3390/jcm11175106. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36079032 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac structure and function across the continuum of glucose metabolism.Physiol Rep. 2025 Jun;13(12):e70429. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70429. Physiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40526029 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tayyareci Y, Yurdakul S, Tayyareci G, Nisanci Y, Umman B, Bugra Z. Impact of myocardial acceleration during isovolumic contraction in evaluating subclinical right ventricular systolic dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Echocardiography. 2010;27:1211–1218. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2010.01237.x. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

