Dexmedetomidine after Cardiac Surgery for Prevention of Delirium (EXACTUM) trial protocol: a multicentre randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 35396310
- PMCID: PMC8996049
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-058968
Dexmedetomidine after Cardiac Surgery for Prevention of Delirium (EXACTUM) trial protocol: a multicentre randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Introduction: Incidence of delirium after cardiac surgery remains high and delirium has a significant burden on short-term and long-term outcomes. Multiple causes can trigger delirium occurence, and it has been hypothesised that sleep disturbances can be one of them. Preserving the circadian rhythm with overnight infusion of low-dose dexmedetomidine has been shown to lower the occurrence of delirium in older patients after non-cardiac surgery. However, these results remain controversial. The aim of this study was to demonstrate the usefulness of sleep induction by overnight infusion of dexmedetomidine to prevent delirium after cardiac surgery.
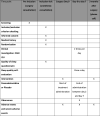
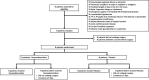
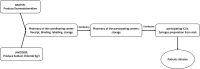
Methods and analysis: Dexmedetomidine after Cardiac Surgery for Prevention of Delirium is an investigator-initiated, randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel, multicentre, double-blinded trial. Nine centres in France will participate in the study. Patients aged 65 years or older and undergoing cardiac surgery will be enrolled in the study. The intervention starts on day 0 (the day of surgery) until intensive care unit (ICU) discharge; the treatment is administered from 20:00 to 08:00 on the next day. Infusion rate is modified by the treating nurse or the clinician with an objective of Richmond Agitation and Sedation Scale score from -1 to +1. The primary outcome is delirium occurrence evaluated with confusion assessment method for the ICU two times per day during 7 days following surgery. Secondary outcomes include incidence of agitation related events, self-evaluated quality of sleep, cognitive evaluation 3 months after surgery and quality of life 3 months after surgery. The sample size is 348.
Ethics and dissemination: The study was approved for all participating centers by the French Central Ethics Committee (Comité de Protection des Personnes Ile de France VI, registration number 2018-000850-22). The results will be submitted for publication in peer-reviewed journals.
Trial registration number: NCT03477344.
Keywords: Cardiac surgery; Delirium; Dexmedetomidine; Intensive care.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical