The transcriptome from asexual to sexual in vitro development of Cystoisospora suis (Apicomplexa: Coccidia)
- PMID: 35396557
- PMCID: PMC8993856
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-09714-8
The transcriptome from asexual to sexual in vitro development of Cystoisospora suis (Apicomplexa: Coccidia)
Abstract
The apicomplexan parasite Cystoisospora suis is an enteropathogen of suckling piglets with woldwide distribution. As with all coccidian parasites, its lifecycle is characterized by asexual multiplication followed by sexual development with two morphologically distinct cell types that presumably fuse to form a zygote from which the oocyst arises. However, knowledge of the sexual development of C. suis is still limited. To complement previous in vitro studies, we analysed transcriptional profiles at three different time points of development (corresponding to asexual, immature and mature sexual stages) in vitro via RNASeq. Overall, transcription of genes encoding proteins with important roles in gametes biology, oocyst wall biosynthesis, DNA replication and axonema formation as well as proteins with important roles in merozoite biology was identified. A homologue of an oocyst wall tyrosine rich protein of Toxoplasma gondii was expressed in macrogametes and oocysts of C. suis. We evaluated inhibition of sexual development in a host-free culture for C. suis by antiserum specific to this protein to evaluate whether it could be exploited as a candidate for control strategies against C. suis. Based on these data, targets can be defined for future strategies to interrupt parasite transmission during sexual development.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
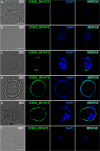
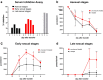
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of sexual stage-specific proteins results in reduced numbers of sexual stages and oocysts of Cystoisospora suis (Apicomplexa: Coccidia) in vitro.Int J Parasitol. 2022 Dec;52(13-14):829-841. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2022.09.006. Epub 2022 Oct 18. Int J Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 36270547
-
Progression of asexual to sexual stages of Cystoisospora suis in a host cell-free environment as a model for Coccidia.Parasitology. 2021 Oct;148(12):1475-1481. doi: 10.1017/S0031182021001074. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Parasitology. 2021. PMID: 34193323 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Cystoisospora suis sexual stages in vitro.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Mar 18;13(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04014-4. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32188507 Free PMC article.
-
Recent achievements and doors opened for coccidian parasite research and development through transcriptomics of enteric sexual stages.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2021 May;243:111373. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2021.111373. Epub 2021 May 4. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 33961917 Review.
-
In vitro cultivation methods for coccidian parasite research.Int J Parasitol. 2023 Aug;53(9):477-489. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2022.10.002. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Int J Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 36400306 Review.
Cited by
-
Unravelling the sexual developmental biology of Cystoisospora suis, a model for comparative coccidian parasite studies.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Oct 25;13:1271731. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1271731. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37953800 Free PMC article.
-
A virus associated with the zoonotic pathogen Plasmodium knowlesi causing human malaria is a member of a diverse and unclassified viral taxon.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 19:2024.09.18.613759. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.18.613759. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Virus Evol. 2024 Nov 06;10(1):veae091. doi: 10.1093/ve/veae091. PMID: 39345442 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Advances towards the complete in vitro life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii.Fac Rev. 2023 Feb 13;12:1. doi: 10.12703/r/12-1. eCollection 2023. Fac Rev. 2023. PMID: 36846606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Toxoplasma gondii´s Biology within the Intestinal Epithelium: intestinal-derived models to unravel sexual differentiation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 May 29;13:1134471. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1134471. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37313339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A virus associated with the zoonotic pathogen Plasmodium knowlesi causing human malaria is a member of a diverse and unclassified viral taxon.Virus Evol. 2024 Nov 6;10(1):veae091. doi: 10.1093/ve/veae091. eCollection 2024. Virus Evol. 2024. PMID: 39619416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barta J, Schrenzel M, Carreno R, Rideout B. The Genus Atoxoplasma (Garnham 1950) as a Junior Objective Synonym of the Genus Isospora (Schneider 1881) Species Infecting Birds and Resurrection of Cystoisospora (Frenkel 1977) as the Correct Genus for Isospora Species Infecting Mammals. J. Parasitol. 2005;91:726–727. doi: 10.1645/GE-3341.1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Joachim A, Shrestha A. Coccidiosis of pigs. In: Dubey JP, editor. Coccidiosis in livestock, poultry, companion animals, and humans. Taylor & Francis Group: Milton Park; 2019. pp. 125–145.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

