Does SARS-CoV-2 affect neurodegenerative disorders? TLR2, a potential receptor for SARS-CoV-2 in the CNS
- PMID: 35396576
- PMCID: PMC8990637
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-022-00755-7
Does SARS-CoV-2 affect neurodegenerative disorders? TLR2, a potential receptor for SARS-CoV-2 in the CNS
Abstract
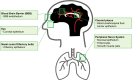
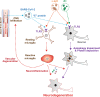
The coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory system coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has created significant challenges for scientists seeking to understand the pathogenic mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 infection and to identify the best therapies for infected patients. Although ACE2 is a known receptor for the virus and has been shown to mediate viral entry into the lungs, accumulating reports highlight the presence of neurological symptoms resulting from infection. As ACE2 expression is low in the central nervous system (CNS), these neurological symptoms are unlikely to be caused by ACE2-virus binding. In this review, we will discuss a proposed interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) in the CNS. TLR2 is an innate immune receptor that recognizes exogenous microbial components but has also been shown to interact with multiple viral components, including the envelope (E) protein of SARS-CoV-2. In addition, TLR2 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD). Based on these observations, we hypothesize that TLR2 may play a critical role in the response to SARS-CoV-2 infiltration in the CNS, thereby resulting in the induction or acceleration of AD and PD pathologies in patients.
© 2022. This is a U.S. government work and not under copyright protection in the U.S.; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploring the Paradox of COVID-19 in Neurological Complications with Emphasis on Parkinson's and Alzheimer's Disease.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Aug 31;2022:3012778. doi: 10.1155/2022/3012778. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36092161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 and neurodegenerative diseases.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Jun;26(12):4535-4544. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202206_29093. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35776055 Review.
-
Ubiquity of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 and upregulation in limbic regions of Alzheimer's disease brain.Folia Neuropathol. 2021;59(3):232-238. doi: 10.5114/fn.2021.109495. Folia Neuropathol. 2021. PMID: 34628788
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) in the Pathogenesis of ARDS in COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:732690. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.732690. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 mediated neurological disorders in COVID-19: Measuring the pathophysiology and immune response.Life Sci. 2022 Nov 1;308:120981. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120981. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36150465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2, long COVID, prion disease and neurodegeneration.Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 27;16:1002770. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1002770. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36238082 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Neurocognitive Impairment After COVID-19: Mechanisms, Phenotypes, and Links to Alzheimer's Disease.Brain Sci. 2025 May 25;15(6):564. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15060564. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40563736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Need for awareness and surveillance of long-term post-COVID neurodegenerative disorders. A position paper from the neuroCOVID-19 task force of the European Academy of Neurology.J Neurol. 2025 May 6;272(6):380. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-13110-3. J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40327103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NLRP3 Inflammasome's Activation in Acute and Chronic Brain Diseases-An Update on Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives with Respect to Other Inflammasomes.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 23;11(4):999. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11040999. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics and systems biology approaches to identify the effects of COVID-19 on neurodegenerative diseases: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 9;101(49):e32100. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032100. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36626425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus Dashboard, https://covid19.who.int (2021).
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19, https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

