Corticocortical innervation subtypes of layer 5 intratelencephalic cells in the murine secondary motor cortex
- PMID: 35396593
- PMCID: PMC9758586
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhac052
Corticocortical innervation subtypes of layer 5 intratelencephalic cells in the murine secondary motor cortex
Abstract
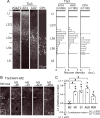
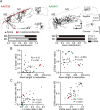
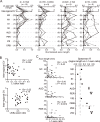
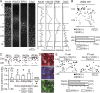
Feedback projections from the secondary motor cortex (M2) to the primary motor and sensory cortices are essential for behavior selection and sensory perception. Intratelencephalic (IT) cells in layer 5 (L5) contribute feedback projections to diverse cortical areas. Here we show that L5 IT cells participating in feedback connections to layer 1 (L1) exhibit distinct projection patterns, genetic profiles, and electrophysiological properties relative to other L5 IT cells. An analysis of the MouseLight database found that L5 IT cells preferentially targeting L1 project broadly to more cortical regions, including the perirhinal and auditory cortices, and innervate a larger volume of striatum than the other L5 IT cells. We found experimentally that in upper L5 (L5a), ER81 (ETV1) was found more often in L1-preferring IT cells, and in IT cells projecting to perirhinal/auditory regions than those projecting to primary motor or somatosensory regions. The perirhinal region-projecting L5a IT cells were synaptically connected to each other and displayed lower input resistance than contra-M2 projecting IT cells including L1-preferring and nonpreferring cells. Our findings suggest that M2-L5a IT L1-preferring cells exhibit stronger ER81 expression and broader cortical/striatal projection fields than do cells that do not preferentially target L1.
Keywords: ER81; MouseLight; corticocortical; corticostriatal; intratelencephalic pyramidal cell.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Institute of Mathematics and its Applications. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ipsi- and contralateral corticocortical projection-dependent subcircuits in layer 2 of the rat frontal cortex.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Oct 1;122(4):1461-1472. doi: 10.1152/jn.00333.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 24. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31339785
-
Direction- and distance-dependent interareal connectivity of pyramidal cell subpopulations in the rat frontal cortex.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 Oct 11;7:164. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00164. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 24137111 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple layer 5 pyramidal cell subtypes relay cortical feedback from secondary to primary motor areas in rats.Cereb Cortex. 2014 Sep;24(9):2362-76. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bht088. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Cereb Cortex. 2014. PMID: 23551921
-
Local connections of excitatory neurons in motor-associated cortical areas of the rat.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 May 28;7:75. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00075. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 23754982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corticostriatal pathways for bilateral sensorimotor functions.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2023 Dec;83:102781. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2023.102781. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37696188 Review.
Cited by
-
Self-supervised predictive learning accounts for cortical layer-specificity.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 4;16(1):6178. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61399-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40615428 Free PMC article.
-
Different effects of I-wave periodicity repetitive TMS on motor cortex interhemispheric interaction.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jun 30;17:1079432. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1079432. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37457007 Free PMC article.
-
Layer 5 Intratelencephalic Neurons in the Motor Cortex Stably Encode Skilled Movement.J Neurosci. 2023 Oct 25;43(43):7130-7148. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0428-23.2023. Epub 2023 Sep 12. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37699714 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic configuration and reconfiguration in the neocortex are spatiotemporally selective.Anat Sci Int. 2024 Jan;99(1):17-33. doi: 10.1007/s12565-023-00743-5. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Anat Sci Int. 2024. PMID: 37837522 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arber S, Ladle DR, Lin JH, Frank E, Jessell TM. ETS gene Er81 controls the formation of functional connections between group Ia sensory afferents and motor neurons. Cell. 2000:101:485–498. - PubMed
-
- Arlotta P, Molyneaux BJ, Chen J, Inoue J, Kominami R, Macklis JD. Neuronal subtype-specific genes that control corticospinal motor neuron development in vivo. Neuron. 2005:45:207–221. - PubMed
-
- Barbas H. General cortical and special prefrontal connections: principles from structure to function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2015:38:269–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

