Antiviral potential of nanoparticles for the treatment of Coronavirus infections
- PMID: 35397331
- PMCID: PMC8957383
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.126977
Antiviral potential of nanoparticles for the treatment of Coronavirus infections
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Antiviral potential of nanoparticles for the treatment of Coronavirus infections" [J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 72 (2022) 1-17].J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2024 May;83:127400. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2024.127400. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38335826 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
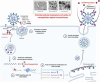
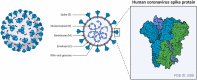
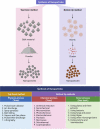
Background: On 31st December 2019 in Wuhan, China, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), was acknowledged. This virus spread quickly throughout the world causing a global pandemic. The World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a pandemic disease on 11th March 2020. Since then, the whole world has come together and have developed several vaccines against this deadly virus. Similarly, several alternative searches for pandemic disease therapeutics are still ongoing. One of them has been identified as nanotechnology. It has demonstrated significant promise for detecting and inhibiting a variety of viruses, including coronaviruses. Several nanoparticles, including gold nanoparticles, silver nanoparticles, quantum dots, carbon dots, graphene oxide nanoparticles, and zinc oxide nanoparticles, have previously demonstrated remarkable antiviral activity against a diverse array of viruses.
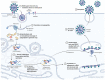
Objective: This review aims to provide a basic and comprehensive overview of COVID-19's initial global outbreak and its mechanism of infiltration into human host cells, as well as the detailed mechanism and inhibitory effects of various nanoparticles against this virus. In addition to nanoparticles, this review focuses on the role of several antiviral drugs used against COVID-19 to date.
Conclusion: COVID-19 has severely disrupted the social and economic lives of people all over the world. Due to a lack of adequate medical facilities, countries have struggled to maintain control of the situation. Neither a drug nor a vaccine has a 100% efficacy rate. As a result, nanotechnology may be a better therapeutic alternative for this pandemic disease.
Keywords: Antiviral activity; COVID-19; Metal nanoparticles; Nanoparticles; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier GmbH. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all listed authors, the corresponding author declares that there is not any sort of financial and non-financial conflict of interest in the subject materials mentioned in this manuscript.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

