Synthesis and characterization of a new Positron emission tomography probe for orexin 2 receptors neuroimaging
- PMID: 35397430
- PMCID: PMC9050936
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105779
Synthesis and characterization of a new Positron emission tomography probe for orexin 2 receptors neuroimaging
Abstract
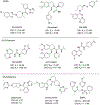
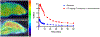
The orexin receptors (OXRs) have been involved in multiple physiological and neuropsychiatric functions. Identification of PET imaging probes specifically targeting OXRs enables us to better understand the OX system. Seltorexant (JNJ-42847922) is a potent OX2R antagonist with the potential to be an OX2R PET imaging probe. Here, we describe the synthesis and characterization of [18F]Seltorexant as an OX2R PET probe. The ex vivo autoradiography studies indicated the good binding specificity of [18F]Seltorexant. In vivo PET imaging of [18F]Seltorexant in rodents showed suitable BBB penetration with the highest brain uptake of %ID/cc = 3.4 at 2 min post-injection in mice. The regional brain biodistribution analysis and blocking studies showed that [18F]Seltorexant had good binding selectivity and specificity. However, pretreatment with unlabelled Seltorexant and P-gp competitor CsA observed significantly increased brain uptake of [18F]Seltorexant, indicating [18F]Seltorexant could interact P-gp at the blood-brain barrier. Our findings demonstrated that [18F]Seltorexant is a potential brain OX2R PET imaging probe, which paves the way for new OX2R PET probes development and OX system investigation.
Keywords: Imaging; Orexin receptors; PET; Radiotracer.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure
We have no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



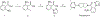
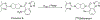
References
-
- Sakurai T; Amemiya A; Ishii M; Matsuzaki I; Chemelli RM; Tanaka H; Williams SC; Richarson JA; Kozlowski GP; Wilson S; Arch JR; Buckingham RE; Haynes AC; Carr SA; Annan RS; McNulty DE; Liu WS; Terrett JA; Elshourbagy NA; Bergsma DJ; Yanagisawa M, Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 1998, 92 (5), 573–585. - PubMed
-
- Sakurai T, Orexins and orexin receptors: implication in feeding behavior. Regul Pept 1999, 85 (1), 25–30. - PubMed
-
- Nishino S, Hypothalamus, hypocretins/orexin, and vigilance control. Handb Clin Neurol 2011, 99, 765–782. - PubMed
-
- Roecker AJ; Cox CD; Coleman PJ, Orexin Receptor Antagonists: New Therapeutic Agents for the Treatment of Insomnia. J Med Chem 2016, 59 (2), 504–530. - PubMed
-
- Brisbare-Roch C; Dingemanse J; Koberstein R; Hoever P; Aissaoui H; Flores S; Mueller C; Nayler O; van Gerven J; de Haas SL; Hess P; Qiu C; Buchmann S; Scherz M; Weller T; Fischli W; Clozel M; Jenck F, Promotion of sleep by targeting the orexin system in rats, dogs and humans. Nat Med 2007, 13 (2), 150–155. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

