Comparison of the effectiveness and duration of anti-RBD SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody response between different types of vaccines: Implications for vaccine strategies
- PMID: 35397946
- PMCID: PMC8971065
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.03.069
Comparison of the effectiveness and duration of anti-RBD SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody response between different types of vaccines: Implications for vaccine strategies
Abstract
Background and objectives: Little is known about the efficacy and durability of anti-RBD IgG antibodies induced by certain SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. It has been shown that neutralizing antibodies are associated with the protection against re-infection. This study aims to compare the mean titers, duration, and efficacy of generating protective anti-RBD IgG antibody response among recipients of Pfizer/BioNTech, AstraZeneca, Sputnik V, Johnson & Johnson, Moderna, and Sinopharm COVID-19 vaccines. In addition, we aimed to compare the susceptibility of getting COVID-19 breakthrough infections after various types of vaccines.
Materials and methods: Samples from 2065 blood bank donors and healthcare workers at King Hussein Cancer Center (KHCC) were collected between February and September 2021. Anti-Spike/RBD IgG levels were measured using Chemiluminescent microparticle-immunoassay (CMIA) (ARCHITECT IgG II Quant test, Abbott, USA).
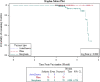
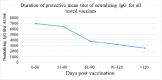
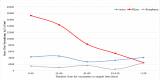
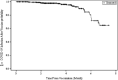
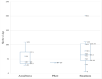
Results: The mean titer of anti-RBD IgG levels was significantly diverse among different types of vaccines. The highest titer level was seen in participants who took a third booster vaccine shot, followed by Pfizer/BioNTech, AstraZeneca, and Sinopharm vaccine. The mean titer levels of anti-RBD IgG antibodies in the Pfizer vaccinated group was the highest after vaccination but started to drop after 60 days from vaccination unlike AstraZeneca and Sinopharm vaccine-induced antibodies where the mean titers continued to be stable until 120 days but their levels were significantly lower. Most of the breakthrough infections were among the Sinopharm vaccinated group and these breakthroughs happened at random times for the three main types of vaccines.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that the mean-titer of anti-RBD IgG levels drop after four months which is the best time to take the additional booster shot from a more potent vaccine type such as mRNA vaccines that might be needed in Jordan and worldwide.
Keywords: Anti-RBD antibody; Antibody titer; Blood bank donors, vaccine; COVID-19; Healthcare workers; IgG; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RBD-specific antibody response after two doses of different SARS-CoV-2 vaccines during the mass vaccination campaign in Mongolia.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 8;18(12):e0295167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295167. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38064430 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of IgA, IgG, and Neutralizing Antibody Responses Following Immunization With Moderna, BioNTech, AstraZeneca, Sputnik-V, Johnson and Johnson, and Sinopharm's COVID-19 Vaccines.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 21;13:917905. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.917905. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35799790 Free PMC article.
-
Seroepidemiological assessment of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine responsiveness and associated factors in the vaccinated community of the Casablanca-Settat Region, Morocco.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 3;14(1):7817. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58498-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38570577 Free PMC article.
-
Saliva is suitable for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies detection after vaccination: A rapid systematic review.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 20;13:1006040. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1006040. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36203571 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 for Pfizer BioNTech, Moderna, and AstraZeneca vaccines: a systematic review.Front Public Health. 2023 Oct 24;11:1229716. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1229716. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37942238 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antibody responses to mRNA versus non-mRNA COVID vaccines among the Mongolian population.IJID Reg. 2023 Sep;8:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2023.05.002. Epub 2023 May 14. IJID Reg. 2023. PMID: 37309454 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical features of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Omicron variant infection in children: an analysis of 201 cases].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Jan 15;25(1):5-10. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2207052. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36655657 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Individuals Infected with SARS-CoV-2 Prior to COVID-19 Vaccination Maintain Vaccine-Induced RBD-Specific Antibody Levels and Viral Neutralization Activity for One Year.Viruses. 2025 Apr 29;17(5):640. doi: 10.3390/v17050640. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40431652 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 DNA Vaccine Encoding RBD-PVXCP Fusion Protein.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 May 23;11(6):1014. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11061014. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37376403 Free PMC article.
-
RBD-specific antibody response after two doses of different SARS-CoV-2 vaccines during the mass vaccination campaign in Mongolia.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 8;18(12):e0295167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295167. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38064430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Center B.D. Brookings Doha Center; Jordan. Doha, Qatar: 2021. Policy and institutional responses to COVID-19 in the Middle East and North Africa.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

