Structural enzymology of cholesterol biosynthesis and storage
- PMID: 35398802
- PMCID: PMC9189044
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2022.102369
Structural enzymology of cholesterol biosynthesis and storage
Abstract
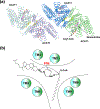
Cholesterol biosynthesis occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Its lego-like construction from water-soluble small metabolites via intermediates of increasing complexity to water-insoluble cholesterol requires numerous distinct enzymes. Dysfunction of the involved enzymes can cause several human inborn defects and diseases. Here, we review recent structures of three key cholesterol biosynthetic enzymes: Squalene epoxidase (SQLE), NAD(P)-dependent steroid dehydrogenase-like (NSDHL), and 3β-hydroxysteroid Δ8-Δ7 isomerase termed EBP. Moreover, we discuss structures of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) enzymes, which are responsible for forming cholesteryl esters from cholesterol to maintain cholesterol homeostasis in the ER. The structures of these enzymes reveal their catalytic mechanism and provide a molecular basis to develop drugs for treating diseases linked to their dysregulation.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement Nothing declared.
Figures


References
-
- Luo J, Yang H and Song BL (2019) Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology - PubMed
-
- Cerqueira NM, Oliveira EF, Gesto DS, Santos-Martins D, Moreira C, Moorthy HN, Ramos MJ and Fernandes PA (2016) Cholesterol Biosynthesis: A Mechanistic Overview. Biochemistry, 55, 5483–5506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

