Efficacy of Remimazolam for Procedural Sedation in American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) I to IV Patients Undergoing Colonoscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35399486
- PMCID: PMC8982285
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.22881
Efficacy of Remimazolam for Procedural Sedation in American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) I to IV Patients Undergoing Colonoscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Remimazolam is made by combining midazolam and remifentanil as an alternative to conventional sedatives. To evaluate the efficacy of remimazolam for sedation in patients undergoing colonoscopy, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of the available randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing remimazolam and midazolam. A search was conducted using PubMed, Cochrane Library, and clinicaltrial.gov from inception till December 26, 2021, for RCTs that investigated the efficacy of remimazolam during the above-mentioned procedure. There was no restriction of language. A quality assessment was performed using the Cochrane Risk-of-Bias tool. The data were pooled, and a meta-analysis was completed. The systemic review was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systemic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guideline statement. Three randomized controlled trials involving 539 patients were included in the meta-analysis. Compared with midazolam during colonoscopy, remimazolam results in reduced need for top-up doses (RR= 3.45, 95% CI=1.07 to 11.14; P=0.04, I2=84%). The need for rescue medication was reduced with remimazolam as compared to midazolam (RR=2.42, 95%CI=1.04 to 5.61; P=0.04, I2=96%). There was no significant difference observed between the two drugs on completion of colonoscopy and the overall procedural sedation, but the sensitivity analysis favored remimazolam over midazolam for procedural sedation (RR=4.08, 95%CI=2.35 to 7.09; P<0.00001, I2=39%). This analysis demonstrates the advantages of remimazolam over other agents and sets a platform for relevant future studies.
Keywords: meta-analysis; midazolam; procedural sedation; remimazolam; colonoscopy.
Copyright © 2022, Ul-Haque et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
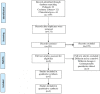

References
-
- AGA Institute review of endoscopic sedation. Cohen LB, Delegge MH, Aisenberg J, Brill JV, Inadomi JM, Kochman ML, Piorkowski JD Jr. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:675–701. - PubMed
-
- Remimazolam: first approval. Keam SJ. Drugs. 2020;80:625–633. - PubMed
-
- A phase IIb study comparing the safety and efficacy of remimazolam and midazolam in patients undergoing colonoscopy. Pambianco DJ, Borkett KM, Riff DS, Winkle PJ, Schwartz HI, Melson TI, Wilhelm-Ogunbiyi K. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;83:984–992. - PubMed
-
- Propofol. [ Aug; 2021 ];https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Propofol 2005
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
