Long-term survival and reasons for failure in direct anterior composite restorations: A systematic review
- PMID: 35399771
- PMCID: PMC8989165
- DOI: 10.4103/jcd.jcd_527_21
Long-term survival and reasons for failure in direct anterior composite restorations: A systematic review
Abstract
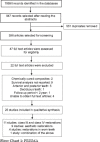
This study investigated the clinical longevity of direct anterior composite restorations. Clinical studies exploring survival of anterior light-cured composite restorations with minimum of 2 years of follow-up were screened and reasons related to failure of direct anterior composite restorations were noted. PubMed, LILIACS, ProQuest, CENTRAL, and MEDLINE databases were searched with no restriction on date. Articles obtainable in the English language solely were enclosed during this study. Furthermore, articles to which reviewers had access were solely enclosed in ProQuest. Reference lists of eligible studies were hand searched. Initially, four reviewers screened the titles/abstracts of 947 studies. Out of those studies, a total of 47 articles were selected for full text reading, from which 25 studies were selected for qualitative synthesis. The studies that were enclosed evaluated the clinical performance of composite class III and class IV restorations (11 studies), which were placed due to caries, fracture, or replaced old restorations, veneers and full coverage restorations placed for esthetic reasons (9 studies), restorations in worn teeth (4 studies) with one study including combination of three type of studies listed above. A total of 75,637 restorations were evaluated and annual failure rates were in the range of 0% to 27.11% with survival rates ranging from 28.6% to 100%. Class III restorations had lower failure rates than alternative restorations. Fracture was the main cause of failure of restorations. The factors related to failure of restoration were adhesive technique, type of composite resin used, replacement of restoration first placed, and time required to make up the restorations.
Keywords: Composite; direct; restoration; survival.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Conservative Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
-
- Mjör IA, Shen C, Eliasson ST, Richter S. Placement and replacement of restorations in general dental practice in Iceland. Oper Dent. 2002;27:117–23. - PubMed
-
- Ferracane JL. Resin composite – State of the art. Dent Mater J. 2011;27:29–38. - PubMed
-
- Moura FR, Romano AR, Lund RG, Piva E, Rodrigues Júnior SA, Demarco FF. Three-year clinical performance of composite restorations placed by undergraduate dental students. Braz Dent J. 2011;22:111–6. - PubMed
-
- Baldissera RA, Corrêa MB, Schuch HS, Collares K, Nascimento GG, Jardim PS, et al. Are there universal restorative composites for anterior and posterior teeth? J Dent. 2013;41:1027–35. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources