The Resting-State Brain Network Functional Connectivity Changes in Patients With Acute Thyrotoxic Myopathy Based on Independent Component Analysis
- PMID: 35399921
- PMCID: PMC8986988
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.829411
The Resting-State Brain Network Functional Connectivity Changes in Patients With Acute Thyrotoxic Myopathy Based on Independent Component Analysis
Abstract
Objective: The independent component analysis (ICA) was applied to explore the correlation between clinical manifestation and the functional connectivity changes of the sensorimotor network (SMN) and left frontoparietal network (LFPN) in patients with acute thyrotoxic myopathy (ATM), which was expected to provide a functional imaging basis for the exploration of the pathophysiological mechanism of ATM.
Methods: 13 ATM patients (ATM) and 12 non-ATM patients (nATM) who met the diagnostic and inclusion criteria were enrolled. Their resting-state brain function images were obtained with resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI). GIFT software was used for independent component analysis to obtain the brain regions with SMN and LFPN changes. The correlation between the functional connectivity of these brain regions and clinical indicators was calculated.
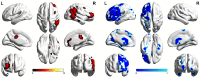
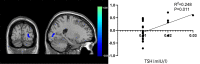
Results: The SMN functional connectivity of ATM patients was increased at the posterior lobe of cerebellum, anterior lobe of cerebellum, right superior temporal gyrus, left cingulate gyrus, left precuneus, and left postcentral gyrus compared with that of nATM patients. However, it was decreased at the occipital lobe, right dorsolateral superior frontal gyrus, paracentral lobule, angular gyrus, and superior parietal gyrus (FDR correction, P<0.05). The LFPN functional connectivity of ATM patients was increased at the posterior lobe of cerebellum, middle temporal gyrus, inferior temporal gyrus, and right cingulate gyrus compared with that of nATM patients; but was decreased at frontal lobe, parahippocampal gyrus, precentral gyrus and postcentral gyrus (FDR correction, P<0.05) Correlation analysis results showed that the enhancement of SMN functional connection at right superior temporal gyrus was significantly negatively correlated with the free thyroxine level, and the decrease of SMN functional connectivity at occipital lobe was significantly positively correlated to the thyroid stimulating hormone level. The SMN and LFPN functional connectivity changes in other brain regions were not found to be significantly correlated with thyroid function parameters.
Conclusion: The bulbar paralysis (such as dysphagia, dysarthria) in ATM patients may be related to the functional connectivity changes of resting-state SMN and LFPN. The fMRI is expected to be one of the objective imaging indicators for the early clinical intervention of ATM patients.
Keywords: (ICA) independent component analysis; (LFPN) left frontoparietal network; (SMN) sensorimotor network; acute thyrotoxic myopathy; functional magnetic resonance imaging; resting-state brain network.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Ling, Huang, Liang, Qin, Luo and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aberrant functional connectivity within and between brain networks in patients with early-onset bipolar disorder.J Affect Disord. 2023 Oct 1;338:41-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.05.057. Epub 2023 May 29. J Affect Disord. 2023. PMID: 37257780
-
Brain functional connectivity during storage based on resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging with synchronous urodynamic testing in healthy volunteers.Brain Imaging Behav. 2021 Jun;15(3):1676-1684. doi: 10.1007/s11682-020-00362-y. Brain Imaging Behav. 2021. PMID: 32725470
-
Abnormal brain regional activity in acute thyrotoxic myopathy assessed by resting-state functional MRI.Acta Radiol. 2024 Nov;65(11):1347-1358. doi: 10.1177/02841851241280115. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Acta Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39314056
-
Resting-state abnormalities in functional connectivity of the default mode network in migraine: A meta-analysis.Front Neurosci. 2023 Mar 1;17:1136790. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1136790. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36937687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neural basis of pain during labor.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 May;228(5S):S1241-S1245. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2023.02.012. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023. PMID: 36948996 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain functional connectivity in hyperthyroid patients: systematic review.Front Neurosci. 2024 Apr 24;18:1383355. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1383355. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38726033 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated serum CD40 as a potential biomarker for the differential diagnosis of acute thyrotoxic myopathy.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 12;15(1):8467. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93522-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40069315 Free PMC article.
-
Independent Component Analysis (ICA) With Covariates Strengthens Behavioral Links in Electroencephalography (EEG) Connectivity.Cureus. 2025 Jun 22;17(6):e86533. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86533. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40698201 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal static and dynamic functional network connectivity in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Oct 17;14:1009232. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1009232. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36325191 Free PMC article.
-
Functional decoding and meta-analytic connectivity modeling in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 15;10(1):e23749. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23749. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38226223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou HY, Liang XH, Qin SZ, Qin YF, Zhang J, Zhou J, et al. . Clinical Analysis of 69 Patients With Acute Hyperthyroid Myopathy and Its Treatment. Chin J Endocrinol Metab (2012) 11):896–8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2012.11.008 - DOI
-
- Zhang ZH, Cao CY, Ye SZ. A Case Report of Acute Thyrotoxic Myopathy. Chin J Endocrinol Metab (1987) 02):57–8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.1987.02.131 - DOI
-
- Kuang YQ, Huang XM, Li X, Huang ZX, Ye W, Lu DC, et al. . Changes in the Degree Centrality in Acute Thyrotoxic Myopathy Assessed by Resting-State Functional MRI. J Pract Med (2020) 36(10):1360–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006⁃5725.2020.10.018 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

