A Web Server for GPCR-GPCR Interaction Pair Prediction
- PMID: 35399947
- PMCID: PMC8989088
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.825195
A Web Server for GPCR-GPCR Interaction Pair Prediction
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: A Web Server for GPCR-GPCR Interaction Pair Prediction.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 1;13:944910. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.944910. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35721717 Free PMC article.
Abstract
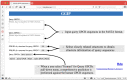
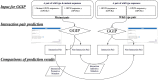
The GGIP web server (https://protein.b.dendai.ac.jp/GGIP/) provides a web application for GPCR-GPCR interaction pair prediction by a support vector machine. The server accepts two sequences in the FASTA format. It responds with a prediction that the input GPCR sequence pair either interacts or not. GPCRs predicted to interact with the monomers constituting the pair are also shown when query sequences are human GPCRs. The server is simple to use. A pair of amino acid sequences in the FASTA format is pasted into the text area, a PDB ID for a template structure is selected, and then the 'Execute' button is clicked. The server quickly responds with a prediction result. The major advantage of this server is that it employs the GGIP software, which is presently the only method for predicting GPCR-interaction pairs. Our web server is freely available with no login requirement. In this article, we introduce some application examples of GGIP for disease-associated mutation analysis.
Keywords: GPCR; bioinformatics; disease-associated mutation; machine learning; membrane protein; prediction; protein-protein interaction; web service.
Copyright © 2022 Nemoto, Yamanishi, Limviphuvadh, Fujishiro, Shimamura, Fukushima and Toh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CENTROIDFOLD: a web server for RNA secondary structure prediction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jul;37(Web Server issue):W277-80. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp367. Epub 2009 May 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19435882 Free PMC article.
-
GGIP: Structure and sequence-based GPCR-GPCR interaction pair predictor.Proteins. 2016 Sep;84(9):1224-33. doi: 10.1002/prot.25071. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Proteins. 2016. PMID: 27191053
-
Update of the GRIP web service.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2020 Aug;40(4):348-356. doi: 10.1080/10799893.2020.1734821. Epub 2020 Mar 8. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2020. PMID: 32148150
-
Bioinformatics tools for predicting GPCR gene functions.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;796:205-24. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-7423-0_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24158807 Review.
-
Impact of Machine Learning-Associated Research Strategies on the Identification of Peptide-Receptor Interactions in the Post-Omics Era.Neuroendocrinology. 2023;113(2):251-261. doi: 10.1159/000518572. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Neuroendocrinology. 2023. PMID: 34348315 Review.
Cited by
-
Orphan G protein-coupled receptors: the ongoing search for a home.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 29;15:1349097. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1349097. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38495099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decrypting orphan GPCR drug discovery via multitask learning.J Cheminform. 2024 Jan 23;16(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13321-024-00806-3. J Cheminform. 2024. PMID: 38263092 Free PMC article.
-
The oxytocin receptor represents a key hub in the GPCR heteroreceptor network: potential relevance for brain and behavior.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Dec 8;15:1055344. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1055344. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36618821 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources