Association of Healthy Diet and Physical Activity With Breast Cancer: Lifestyle Interventions and Oncology Education
- PMID: 35400043
- PMCID: PMC8984028
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.797794
Association of Healthy Diet and Physical Activity With Breast Cancer: Lifestyle Interventions and Oncology Education
Abstract
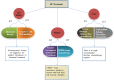
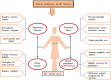
Global cancer statistics suggest that breast cancer (BC) is the most diagnosed cancer in women, with an estimated 2. 3 million new cases reported in 2020. Observational evidence shows a clear link between prevention and development of invasive BC and lifestyle-based interventions such as a healthy diet and physical activity. The recent findings reveal that even minimal amounts of daily exercise and a healthy diet reduced the risk of BC, mitigated the side effects of cancer treatment, and stopped the recurrence of cancer in the survivors. Despite the myriad benefits, the implementation of these lifestyle interventions in at-risk and survivor populations has been limited to date. Given the need to disseminate information about the role of physical activity and nutrition in BC reduction, the review aimed to present the recent scientific outreach and update on associations between the lifestyle interventions and BC outcomes to narrow the gap and strengthen the understanding more clearly. This review covers more direct, detailed, and updated scientific literature to respond to frequently asked questions related to the daily lifestyle-based interventions and their impact on BC risk and survivors. This review also highlights the importance of the oncology provider's job and how oncology education can reduce the BC burden.
Keywords: breast cancer; diet; lifestyle; oncology education; physical activity.
Copyright © 2022 Jia, Liu, Fan, Wang and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Examining Lifestyle Information Sources, Needs, and Preferences among Breast Cancer Survivors in Northern British Columbia.Can J Diet Pract Res. 2017 Dec 1;78(4):212-216. doi: 10.3148/cjdpr-2017-016. Epub 2017 May 24. Can J Diet Pract Res. 2017. PMID: 28537139
-
Effect of healthy diet and exercise on chemotherapy completion rate in women with breast cancer: The Lifestyle, Exercise and Nutrition Early after Diagnosis (LEANer) study: Study protocol for a randomized clinical trial.Contemp Clin Trials. 2021 Oct;109:106508. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2021.106508. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Contemp Clin Trials. 2021. PMID: 34274495 Free PMC article.
-
Weight Management and Physical Activity for Breast Cancer Prevention and Control.Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2019 Jan;39:e22-e33. doi: 10.1200/EDBK_237423. Epub 2019 May 17. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2019. PMID: 31099634 Review.
-
Quality of Life in Women Diagnosed with Breast Cancer after a 12-Month Treatment of Lifestyle Modifications.Nutrients. 2020 Dec 31;13(1):136. doi: 10.3390/nu13010136. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33396551 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Breast Cancer Diet "BCD": A Review of Healthy Dietary Patterns to Prevent Breast Cancer Recurrence and Reduce Mortality.Nutrients. 2022 Jan 21;14(3):476. doi: 10.3390/nu14030476. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35276833 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nutrition Intervention and Microbiome Modulation in the Management of Breast Cancer.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 10;16(16):2644. doi: 10.3390/nu16162644. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39203781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evaluation of the effectiveness of a health promotion training on breast cancer survivors.J Educ Health Promot. 2024 Feb 7;13:31. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_960_23. eCollection 2024. J Educ Health Promot. 2024. PMID: 38545312 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the effective behaviour change techniques in nutrition and physical activity interventions for the treatment of overweight/obesity in post-treatment breast cancer survivors: a systematic review.Cancer Causes Control. 2023 Aug;34(8):683-703. doi: 10.1007/s10552-023-01707-w. Epub 2023 May 6. Cancer Causes Control. 2023. PMID: 37149509 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary intervention on human diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Mar 11;9(1):59. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01771-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38462638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Creatine and Resistance Training: A Combined Approach to Attenuate Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 19;15(18):4048. doi: 10.3390/nu15184048. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Narod SA, Iqbal J, Miller AB. Why have breast cancer mortality rates declined? J Cancer Policy. (2015) 5:8–17. 10.1016/j.jcpo.2015.03.002 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

