A porcine lymphoma-derived cell line co-expressing IgM, IgG and IgA
- PMID: 35400671
- PMCID: PMC9246694
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.21-0508
A porcine lymphoma-derived cell line co-expressing IgM, IgG and IgA
Abstract
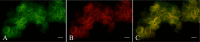
A cell line (PL38PB) was established from blood samples of a 6-month-old pig that was diagnosed with lymphoma with CD5 expression. Histopathological examination revealed neoplastic lesions in the spleen, liver and lymph nodes. Tumor cells were immunohistochemically positive for CD20 and immunoglobulin heavy chains (μ, γ and α). Membranous CD5 and cytoplasmic Immunoglobulin M (IgM), Immunoglobulin G (IgG) and Immunoglobulin A (IgA) were detected in PL38PB cells by flow cytometry. In addition, the cytoplasm of PL38PB cells were positive for IgM, IgG and IgA by immunofluorescent. However, no Ig secretion was detected in culture supernatant by Ouchterlony gel diffusion method. Results suggest that PL38PB cells express three Ig isotypes that are produced but not secreted.
Keywords: CD5; cell line; immunoglobulin; lymphoma; swine.
Figures






References
-
- Chan J. K. C.2007. Tumors of the lymphoreticular system. pp. 1139–1288. In: Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors, 3rd ed. (Fletcher, C. D. M. ed.), Churchill Livingstone, London.
-
- Feller A. C., Diebold J.2004. Variant: Lymphoplasmacytoid lymphoma (immunocytoma). pp. 31–34. In: Histopathology of Nodal and Extranodal Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas, 3rd ed., Springer, Berlin.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

