Delayed Graft Function Under the Microscope: Surveillance Biopsies in Kidney Transplantation
- PMID: 35401043
- PMCID: PMC8988887
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2022.10344
Delayed Graft Function Under the Microscope: Surveillance Biopsies in Kidney Transplantation
Abstract
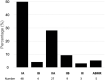
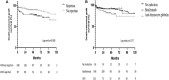
Delayed graft function (DGF) is a common complication of kidney transplantation and frequently leads to the necessity of surveillance biopsies. The purpose of this study is to describe the histological findings in surveillance biopsies of deceased donor kidney transplant recipients and evaluate the risk factors for graft outcomes. This is a monocentric, retrospective study including kidney transplant recipients that underwent a graft biopsy during the DGF period between January 2006 and July 2019. 356 biopsies were performed in 335 deceased donor transplant recipients. Biopsies were analyzed according to the Banff classification. The main histological findings were: acute tubular necrosis in 150 biopsies (42.1%), acute rejection in 96 biopsies (26.9%), and borderline findings in 91 biopsies (25.5%). In the multivariate analysis, recipient age (p = 0.028) and DGF duration (p = 0.005) were associated with rejection, antibody-induction with anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG) was protective (p = 0.001). The occurrence of rejection was associated with lower death-censored graft survival (log-rank; p = 0.009). Surveillance biopsies of kidney grafts experiencing DGF remain an essential tool for the care of kidney transplant recipients. The recipient's age and duration of DGF are independent risk factors for acute rejection, while antibody-induction therapy with ATG is associated with protection from its occurrence.
Keywords: acute rejection; delayed graft function; immunosuppression; renal biopsy; renal transplantation.
Copyright © 2022 Castro Filho, Pompeo, Machado, Gonçalves, Bauer and Manfro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Purnell TS, Auguste P, Crews DC, Lamprea-Montealegre J, Olufade T, Greer R, et al. Comparison of Life Participation Activities Among Adults Treated by Hemodialysis, Peritoneal Dialysis, and Kidney Transplantation: a Systematic Review. Am J Kidney Dis (2013). 62:953–73. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.03.022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- ABTO (Brazilian Organ Transplantation Society). Organ Transplantation in Brazil (2012-2019). In: Brazilian Transplantation Registry. São Paulo, SP: ABTO; (2019).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

