A Novel Small Molecular Inhibitor of DNMT1 Enhances the Antitumor Effect of Radiofrequency Ablation in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 35401185
- PMCID: PMC8983860
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.863339
A Novel Small Molecular Inhibitor of DNMT1 Enhances the Antitumor Effect of Radiofrequency Ablation in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
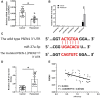
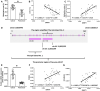
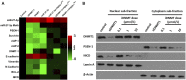
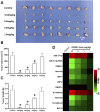
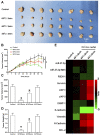
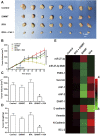
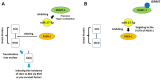
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a relatively new and effective therapeutic strategy for treating lung squamous cell carcinomas (LSCCs). However, RFA is rarely used in the clinic for LSCC which still suffers from a lack of effective comprehensive treatment strategies. In the present work, we investigate iDNMT, a novel small molecular inhibitor of DNMT1 with a unique structure. In clinical LSCC specimens, endogenous DNMT1 was positively associated with methylation rates of miR-27-3p's promoter. Moreover, endogenous DNMT1 was negatively correlated with miR-27-3p expression which targets PSEN-1, the catalytic subunit of γ-secretase, which mediates the cleavage and activation of the Notch pathway. We found that DNMT1 increased activation of the Notch pathway in clinical LSCC samples while downregulating miR-27-3p expression and hypermethylation of miR-27-3p's promoter. In addition of inhibiting activation of the Notch pathway by repressing methylation of the miR-27-3p promoter, treatment of LSCC cells with iDNMT1 also enhanced the sensitivity of LSCC tumor tissues to RFA treatment. These data suggest that iDNMT-induced inhibition of DNMT-1 enhances miR-27-3p expression in LSCC to inhibit activation of the Notch pathway. Furthermore, the combination of iDNMT and RFA may be a promising therapeutic strategy for LSCC.
Keywords: DNA methyltransferase 1; Notch pathway; lung squamous cell carcinoma; radiofrequency ablation; small molecular inhibitor.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Ding, Chen, Wang, Yang and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RUNX3 inhibits laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma malignancy under the regulation of miR-148a-3p/DNMT1 axis.Cell Biochem Funct. 2016 Dec;34(8):597-605. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3233. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Cell Biochem Funct. 2016. PMID: 27859417
-
Anlotinib enhances the antitumor activity of radiofrequency ablation on lung squamous cell carcinoma.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Feb;164:105392. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105392. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33348023
-
Regulation of laryngeal squamous cell cancer progression by the lncRNA H19/miR-148a-3p/DNMT1 axis.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 8;7(10):11553-66. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7270. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26872375 Free PMC article.
-
miR-27-3p Enhances the Sensitivity of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to the Antitumor Agent Olaparib by Targeting PSEN-1, the Catalytic Subunit of Γ-Secretase.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 8;11:694491. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.694491. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34169001 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-clinical lung squamous cell carcinoma mouse models to identify novel biomarkers and therapeutic interventions.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 25;13:1260411. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1260411. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37817767 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MTBP enhances the activation of transcription factor ETS-1 and promotes the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 29;12:985082. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.985082. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36106099 Free PMC article.
-
The role of DNA methylation and DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) as potential biomarker and therapeutic target in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Heliyon. 2024 Sep 27;10(19):e38663. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38663. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39403460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypermethylation of the Promoter Region of miR-23 Enhances the Metastasis and Proliferation of Multiple Myeloma Cells via the Aberrant Expression of uPA.Front Oncol. 2022 May 30;12:835299. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.835299. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35707350 Free PMC article.
-
NIO-1, A Novel Inhibitor of OCT1, Enhances the Antitumor Action of Radiofrequency Ablation against Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Curr Mol Med. 2024;24(5):637-647. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666230526154739. Curr Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37246325
-
DNMT1-targeting remodeling global DNA hypomethylation for enhanced tumor suppression and circumvented toxicity in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2024 May 16;23(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01993-1. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38755637 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An L., Li D. D., Chu H. X., Zhang Q., Wang C. L., Fan Y. H., et al. (2017). Terfenadine Combined with Epirubicin Impedes the Chemo-Resistant Human Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Both In Vitro and In Vivo through EMT and Notch Reversal. Pharmacol. Res. 124, 105–115. 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.07.021 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baas P., Scherpereel A., Nowak A. K., Fujimoto N., Peters S., Tsao A. S., et al. (2021). First-line Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Unresectable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): a Multicentre, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 397 (10272), 375–386. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32714-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cazalas G., Jambon E., Coussy A., Le Bras Y., Petitpierre F., Berhnard J. C., et al. (2021). Local Recurrence and Other Oncologic Outcomes after Percutaneous Image-Guided Tumor Ablations on stageT1b Renal Cell Carcinoma: a Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Hyperthermia 38 (1), 1295–1303. 10.1080/02656736.2021.1970826 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

