Defining Molecular Treatment Targets for Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: Uncovering Adhesion Molecules
- PMID: 35401223
- PMCID: PMC8990855
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.780855
Defining Molecular Treatment Targets for Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: Uncovering Adhesion Molecules
Abstract
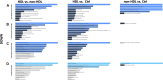
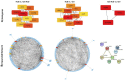
Bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is a debilitating pain syndrome of unknown etiology that predominantly affects females. Clinically, BPS/IC presents in a wide spectrum where all patients report severe bladder pain together with one or more urinary tract symptoms. On bladder examination, some have normal-appearing bladders on cystoscopy, whereas others may have severely inflamed bladder walls with easily bleeding areas (glomerulations) and ulcerations (Hunner's lesion). Thus, the reported prevalence of BPS/IC is also highly variable, between 0.06% and 30%. Nevertheless, it is rightly defined as a rare disease (ORPHA:37202). The aetiopathogenesis of BPS/IC remains largely unknown. Current treatment is mainly symptomatic and palliative, which certainly adds to the suffering of patients. BPS/IC is known to have a genetic component. However, the genes responsible are not defined yet. In addition to traditional genetic approaches, novel research methodologies involving bioinformatics are evaluated to elucidate the genetic basis of BPS/IC. This article aims to review the current evidence on the genetic basis of BPS/IC to determine the most promising targets for possible novel treatments.
Keywords: adhesion molecules; bioinformatics; gene expression; rare urinary disease; targeted treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Inal-Gultekin, Gormez and Mangir.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cystoscopic characteristic findings of interstitial cystitis and clinical implications.Tzu Chi Med J. 2023 Aug 22;36(1):30-37. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_172_23. eCollection 2024 Jan-Mar. Tzu Chi Med J. 2023. PMID: 38406570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological management of interstitial cystitis /bladder pain syndrome and the role cyclosporine and other immunomodulating drugs play.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018 May;11(5):495-505. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2018.1457435. Epub 2018 Apr 9. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29575959 Review.
-
Clinical characterization of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome in women based on the presence or absence of Hunner lesions and glomerulations.Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2021 Jan;13(1):139-143. doi: 10.1111/luts.12344. Epub 2020 Aug 23. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2021. PMID: 32830459
-
Low-pressure hydrodistension induces bladder glomerulations in female patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome.Neurourol Urodyn. 2022 Jan;41(1):296-305. doi: 10.1002/nau.24818. Epub 2021 Oct 11. Neurourol Urodyn. 2022. PMID: 34633704
-
Pentosan polysulfate in patients with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis with Hunner's lesions or glomerulations: systematic review and meta-analysis.Ther Adv Urol. 2022 Jun 2;14:17562872221102809. doi: 10.1177/17562872221102809. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Urol. 2022. PMID: 35677571 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potential Role of Macrophage Polarization in the Progression of Hunner-Type Interstitial Cystitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 8;25(2):778. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020778. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255860 Free PMC article.
-
The role of netrin-1 in the diagnosis and prognosis of bladder pain syndrome /interstitial cystitis: a comparative study.World J Urol. 2025 Jun 3;43(1):351. doi: 10.1007/s00345-025-05659-5. World J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40459754 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Expression-Based Functional Differences between the Bladder Body and Trigonal Urothelium in Adolescent Female Patients with Micturition Dysfunction.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 17;10(6):1435. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061435. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740457 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive transcriptome profiling of urothelial cells following TNFα stimulation in an in vitro interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome model.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 15;13:960667. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.960667. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36045687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barclay A. N., Birkeland M. L., Brown M. H., Beyers A. D., Davis S. J., Somoza C., et al. (1993). The Leukocyte Antigen Facts Book. New York: Academic Press, 124–127.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

