A Structural and Functional Perspective of Death Receptor 6
- PMID: 35401228
- PMCID: PMC8987162
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.836614
A Structural and Functional Perspective of Death Receptor 6
Abstract
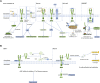
As a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TNFRSF), death receptor 6 (DR6) has a similar structural architecture to other family members. The extracellular region of DR6 contains four cysteine-rich domains, followed by a single-pass transmembrane domain and an intracellular region. Since its discovery, DR6 has become an orphan receptor ubiquitously expressed to transduce unique signaling pathways. Although the free ectodomains of β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) can bind to DR6 to induce apoptotic signals, the natural ligands of DR6 still remain largely unknown. In this review, we focus on recent research progress of structural and functional studies on DR6 for better understanding DR6-mediated signaling and the treatment of DR6-related diseases.
Keywords: DR6; co-receptor; death domain; death receptor; signaling.
Copyright © 2022 Ren, Lin and Yuan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

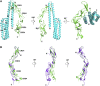
Similar articles
-
The crystal structure of death receptor 6 (DR6): a potential receptor of the amyloid precursor protein (APP).J Mol Biol. 2011 Jun 3;409(2):189-201. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.03.048. Epub 2011 Apr 2. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21463639
-
Agonist antibody activates death receptor 6 downstream signaling involving TRADD recruitment.FEBS Lett. 2014 Jan 31;588(3):401-7. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.12.010. Epub 2013 Dec 24. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24374337
-
Beta amyloid-induced upregulation of death receptor 6 accelerates the toxic effect of N-terminal fragment of amyloid precursor protein.Neurobiol Aging. 2015 Jan;36(1):157-68. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.07.027. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Neurobiol Aging. 2015. PMID: 25150572
-
Structural determinants of DISC function: new insights into death receptor-mediated apoptosis signalling.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Nov;140(2):186-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.06.009. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23845861 Review.
-
Structural Characterization of the p75 Neurotrophin Receptor: A Stranger in the TNFR Superfamily.Vitam Horm. 2017;104:57-87. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Vitam Horm. 2017. PMID: 28215307 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune activation of the p75 neurotrophin receptor: implications in neuroinflammation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Dec 1;16:1305574. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1305574. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38106879 Free PMC article.
-
DR6 Augments Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth, Invasion, and Stemness by Activating AKT/NF-κB Pathway.Biochem Genet. 2025 Feb;63(1):606-622. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10673-0. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 38478147 Free PMC article.
-
The role of tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily in cancer: insights into oncogenesis, progression, and therapeutic strategies.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025 Aug 6;9(1):275. doi: 10.1038/s41698-025-00990-x. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40770489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LPA suppresses HLA-DR expression in human melanoma cells: a potential immune escape mechanism involving LPAR1 and DR6-mediated release of IL-10.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Jan;46(1):222-230. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01373-x. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39187677 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid precursor protein promotes MASH progression by upregulating death receptor 6-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2025 Mar;301(3):108285. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108285. Epub 2025 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39938799 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

