Entactogens: How the Name for a Novel Class of Psychoactive Agents Originated
- PMID: 35401275
- PMCID: PMC8990025
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.863088
Entactogens: How the Name for a Novel Class of Psychoactive Agents Originated
Abstract
At first glance, it appears there is little difference between the molecular structures of methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), which has an N-methyl attached to its amino group, and methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA), a primary amine that is recognized to have hallucinogenic activity. It is known from studies with other hallucinogenic amphetamines that N-methylation of hallucinogenic amphetamines attenuates or abolishes hallucinogenic activity. Nevertheless, MDMA is biologically active and has a potency only slightly less than its MDA parent. Importantly, it is the Ievo-isomer of hallucinogenic phenethylamines that is more biologically active, whereas it is the dextro isomer of MDMA that is more active. This reversal of stereochemistry for the activity of two very closely related molecules is a very powerful clue that their mechanisms of action differ. Finally, extension of the alpha-methyl of hallucinogenic amphetamines to an alpha-ethyl moiety completely abolishes their hallucinogenic activity. Ultimately, we extended the alpha-methyl group of MDMA to an alpha-ethyl to afford a molecule we named (N-Methyl-1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-butanamine (MBDB) that retained significant MDMA-like psychoactivity. Hence, there are three structural features that distinguish MDMA from the hallucinogenic amphetamines: (1) the N-methyl on the basic nitrogen, (2) the reversal of stereochemistry and, (3) tolerance of an alpha-ethyl moiety as contrasted with the alpha-methyl of hallucinogenic phenethylamines. Clearly, MDMA is distinct from classical hallucinogenic phenethylamines in its structure, and its psychopharmacology is also unique. Thus, in 1986 I proposed the name "Entactogen" for the pharmacological class of drugs that includes 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) and other substances with a similar psychopharmacological effect. The name is derived from roots that indicate that entactogens produce a "touching within." Rather than having significant psychostimulant, or hallucinogenic effects, MDMA powerfully promotes affiliative social behavior, has acute anxiolytic effects, and can lead to profound states of introspection and personal reflection. Its mechanism of action is now established as involving transport of MDMA by the neuronal serotonin reuptake carrier followed by carrier-mediated release of stored neuronal serotonin.
Keywords: MBDB; MDMA; entactogen; serotonin; serotonin transporter.
Copyright © 2022 Nichols.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
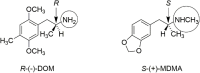
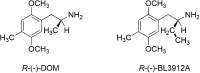
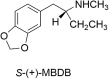
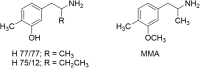
References
-
- Commins DL, Vosmer G, Virus RM, Woolverton WL, Schuster CR, Seiden LS. Biochemical and histological evidence that methylenedioxymethylamphetamine (MDMA) is toxic to neurons in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (1987) 241:338–45. - PubMed
-
- Shulgin AT, Nichols DE. Characterization of Three New Psychotomimetics. In: STILLMAN RC, WILLETTE RE. The Psychopharmacology of Hallucinogens. Elmsford: Pergamon Press Inc; (1978).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

