Different Neural Information Flows Affected by Activity Patterns for Action and Verb Generation
- PMID: 35401310
- PMCID: PMC8987928
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.802756
Different Neural Information Flows Affected by Activity Patterns for Action and Verb Generation
Abstract
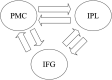
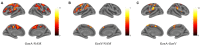
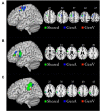
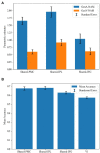
Shared brain regions have been found for processing action and language, including the left inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), the premotor cortex (PMC), and the inferior parietal lobule (IPL). However, in the context of action and language generation that shares the same action semantics, it is unclear whether the activity patterns within the overlapping brain regions would be the same. The changes in effective connectivity affected by these activity patterns are also unclear. In this fMRI study, participants were asked to perform hand action and verb generation tasks toward object pictures. We identified shared and specific brain regions for the two tasks in the left PMC, IFG, and IPL. The mean activation level and multi-voxel pattern analysis revealed that the activity patterns in the shared sub-regions were distinct for the two tasks. The dynamic causal modeling results demonstrated that the information flows for the two tasks were different across the shared sub-regions. These results provided the first neuroimaging evidence that the action and verb generation were task context driven in the shared regions, and the distinct patterns of neural information flow across the PMC-IFG-IPL neural network were affected by the polymodal processing in the shared regions.
Keywords: action; dynamic causal modeling; functional MRI; multi-voxel pattern analysis; verb.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Zhang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Different Neural Activities for Actions and Language within the Shared Brain Regions: Evidence from Action and Verb Generation.Behav Sci (Basel). 2022 Jul 21;12(7):243. doi: 10.3390/bs12070243. Behav Sci (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35877314 Free PMC article.
-
Different activity patterns for action and language within their shared neural areas: An fMRI study on action observation and language phonology.Neuropsychologia. 2017 May;99:112-120. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.02.025. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Neuropsychologia. 2017. PMID: 28259773
-
ACC and IPL networks in the perception of the faces of parents during selective tasks.Brain Imaging Behav. 2016 Dec;10(4):1172-1183. doi: 10.1007/s11682-015-9486-1. Brain Imaging Behav. 2016. PMID: 26613720
-
Nouns and verbs in the brain: grammatical class and task specific effects as revealed by fMRI.Cogn Neuropsychol. 2008 Jun;25(4):528-58. doi: 10.1080/02643290701674943. Cogn Neuropsychol. 2008. PMID: 19086201
-
Neural Correlates of Causal Inferences in Discourse Understanding and Logical Problem-Solving: A Meta-Analysis Study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Jun 23;15:666179. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.666179. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34248525 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mapping relational links between motor imagery, action observation, action-related language, and action execution.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Nov 4;16:984053. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.984053. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36466617 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

