Pangenome Analysis of the Soilborne Fungal Phytopathogen Rhizoctonia solani and Development of a Comprehensive Web Resource: RsolaniDB
- PMID: 35401459
- PMCID: PMC8992008
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.839524
Pangenome Analysis of the Soilborne Fungal Phytopathogen Rhizoctonia solani and Development of a Comprehensive Web Resource: RsolaniDB
Abstract
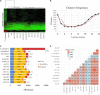
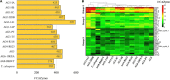
Rhizoctonia solani is a collective group of genetically and pathologically diverse basidiomycetous fungi that damage economically important crops. Its isolates are classified into 13 Anastomosis Groups (AGs) and subgroups having distinctive morphology and host ranges. The genetic factors driving the unique features of R. solani pathology are not well characterized due to the limited availability of its annotated genomes. Therefore, we performed genome sequencing, assembly, annotation and functional analysis of 12 R. solani isolates covering 7 AGs and select subgroups (AG1-IA; AG1-IB; AG1-IC; AG2-2IIIB; AG3-PT, isolates Rhs 1AP and the hypovirulent Rhs1A1; AG3-TB; AG4-HG-I, isolates Rs23 and R118-11; AG5; AG6; and AG8), in which six genomes are reported for the first time. Using a pangenome comparative analysis of 12 R. solani isolates and 15 other Basidiomycetes, we defined the unique and shared secretomes, CAZymes, and effectors across the AGs. We have also elucidated the R. solani-derived factors potentially involved in determining AG-specific host preference, and the attributes distinguishing them from other Basidiomycetes. Finally, we present the largest repertoire of R. solani genomes and their annotated components as a comprehensive database, viz. RsolaniDB, with tools for large-scale data mining, functional enrichment and sequence analysis not available with other state-of-the-art platforms.
Keywords: NGS—next generation sequencing; Rhizoctonia solani; basidiomycetous fungi; genome database; genomics; pangenome analyses; pathogenicity genes; soilborne plant pathogen.
Copyright © 2022 Kaushik, Roberts, Ramaprasad, Mfarrej, Nair, Lakshman and Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Alexa A., Rahnenführer J. (2009). Gene set enrichment analysis with topGO. Bioconductor Improv 27 1–26.
-
- Anderson J. P., Hane J. K., Stoll T., Pain N., Hastie M. L., Kaur P., et al. (2016). Proteomic analysis of Rhizoctonia solani identifies infection-specific, redox associated proteins and insight into adaptation to different plant hosts. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 15 1188–1203. 10.1074/mcp.M115.054502 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrews S. (2020). Babraham bioinformatics – FastQC a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Soil 5 47–81. 10.1016/0038-0717(73)90093-X - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

