Application of Next Generation Sequencing for Diagnosis and Clinical Management of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis: Updates on Recent Developments in the Field
- PMID: 35401475
- PMCID: PMC8988194
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.775030
Application of Next Generation Sequencing for Diagnosis and Clinical Management of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis: Updates on Recent Developments in the Field
Abstract
The World Health Organization's End TB Strategy prioritizes universal access to an early diagnosis and comprehensive drug susceptibility testing (DST) for all individuals with tuberculosis (TB) as a key component of integrated, patient-centered TB care. Next generation whole genome sequencing (WGS) and its associated technology has demonstrated exceptional potential for reliable and comprehensive resistance prediction for Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates, allowing for accurate clinical decisions. This review presents a descriptive analysis of research describing the potential of WGS to accelerate delivery of individualized care, recent advances in sputum-based WGS technology and the role of targeted sequencing for resistance detection. We provide an update on recent research describing the mechanisms of resistance to new and repurposed drugs and the dynamics of mixed infections and its potential implication on TB diagnosis and treatment. Whilst the studies reviewed here have greatly improved our understanding of recent advances in this arena, it highlights significant challenges that remain. The wide-spread introduction of new drugs in the absence of standardized DST has led to rapid emergence of drug resistance. This review highlights apparent gaps in our knowledge of the mechanisms contributing to resistance for these new drugs and challenges that limit the clinical utility of next generation sequencing techniques. It is recommended that a combination of genotypic and phenotypic techniques is warranted to monitor treatment response, curb emerging resistance and further dissemination of drug resistance.
Keywords: drug-resistance; mixed infection; next-generation sequencing; resistance mechanisms; targeted sequencing; tuberculosis; whole genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2022 Dookie, Khan, Padayatchi and Naidoo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
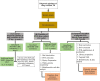
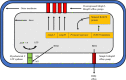
References
-
- Ahmad N., Ahuja S. D., Akkerman O. W., Alffenaar J. W. C., Anderson L. F., Baghaei P., et al. (2018). Treatment correlates of successful outcomes in pulmonary multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Lancet 392 821–834. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31644-31641 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

