Vaccines as a Strategy to Control Trichinellosis
- PMID: 35401479
- PMCID: PMC8984473
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.857786
Vaccines as a Strategy to Control Trichinellosis
Abstract
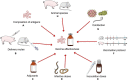
Trichinellosis caused by Trichinella spiralis is a worldwide food-borne parasitic zoonosis. Several approaches have been performed to control T. spiralis infection, including veterinary vaccines, which contribute to improving animal health and increasing public health by preventing the transmission of trichinellosis from animals to humans. In the past several decades, many vaccine studies have been performed in effort to control T. spiralis infection by reducing the muscle larvae and adult worms burden. Various candidate antigens, selected from excretory-secretory (ES) products and different functional proteins involved in the process of establishing infection have been investigated in rodent or swine models to explore their protective effect against T. spiralis infection. Moreover, different types of vaccines have been developed to improve the protective effect against T. spiralis infection in rodent or swine models, such as live attenuated vaccines, natural antigen vaccines, recombinant protein vaccines, DNA vaccines, and synthesized epitope vaccines. However, few studies of T. spiralis vaccines have been performed in pigs, and future research should focus on exploring the protective effect of different types of vaccines in swine models. Here, we present an overview of the strategies for the development of effective T. spiralis vaccines and summarize the factors of influencing the effectiveness of vaccines. We also discuss several propositions in improving the effectiveness of vaccines and may provide a route map for future T. spiralis vaccines development.
Keywords: Trichinella spiralis; antigens; effectiveness; trichinellosis; vaccines.
Copyright © 2022 Tang, Li, Li, Xie, Guan, Zhao, Yang, Liu and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vaccines against Trichinella spiralis: Progress, challenges and future prospects.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2018 Dec;65(6):1447-1458. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12917. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2018. PMID: 29873198 Review.
-
[The usefulness of ELISA test for early serological detection of Trichinella spp. infection in pigs].Wiad Parazytol. 2007;53(2):149-51. Wiad Parazytol. 2007. PMID: 17912813 Polish.
-
Molecular Characterization of Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate Aldolase From Trichinella spiralis and Its Potential in Inducing Immune Protection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Apr 24;9:122. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00122. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31069178 Free PMC article.
-
[The influence of the procedure of excretory-secretory L1 trichinella spiralis antigen preparation on the efficiency of an ELISA test in pigs].Wiad Parazytol. 2006;52(3):219-30. Wiad Parazytol. 2006. PMID: 17432246 Polish.
-
Induction of protection in murine experimental models against Trichinella spiralis: an up-to-date review.J Helminthol. 2015 Sep;89(5):526-39. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X15000140. Epub 2015 Mar 12. J Helminthol. 2015. PMID: 25761655 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel C-type lectin from Trichinella spiralis mediates larval invasion of host intestinal epithelial cells.Vet Res. 2022 Oct 18;53(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01104-2. Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 36258242 Free PMC article.
-
An Update in Knowledge of Pigs as the Source of Zoonotic Pathogens.Animals (Basel). 2023 Oct 20;13(20):3281. doi: 10.3390/ani13203281. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant Live-Attenuated Salmonella Vaccine for Veterinary Use.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Nov 26;12(12):1319. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12121319. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39771981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EmCyclinD-EmCDK4/6 complex is involved in the host EGF-mediated proliferation of Echinococcus multilocularis germinative cells via the EGFR-ERK pathway.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 4;13:968872. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.968872. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36033888 Free PMC article.
-
Oral immunization of mice with recombinant Lactobacillus plantarum expressing a Trichinella spiralis galectin induces an immune protection against larval challenge.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Dec 20;15(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05597-w. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 36539832 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

