Hydroxychloroquine Alleviates EAU by Inhibiting Uveitogenic T Cells and Ameliorating Retinal Vascular Endothelial Cells Dysfunction
- PMID: 35401507
- PMCID: PMC8989724
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.859260
Hydroxychloroquine Alleviates EAU by Inhibiting Uveitogenic T Cells and Ameliorating Retinal Vascular Endothelial Cells Dysfunction
Abstract
Purpose: Inflammation triggers the activation of CD4+T cells and the breakdown of blood-retinal barrier, thus contributing to the pathology of experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU). We explored the anti-inflammatory effect of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) on EAU and the potential mechanisms active in T cells and retinal vascular endothelial cells (RVECs).
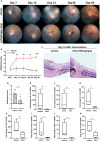
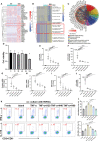
Methods: C57BL/6J mice were immunized with interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein 1-20 (IRBP1-20) to induce EAU and then treated with the vehicle or HCQ (100 mg/kg/day). On day 7, 14, 21, 30 and 60 after immunization, clinical scores were evaluated. On day 14, histopathological scores were assessed, and retinas, spleens, and lymph nodes were collected for quantitative polymerase chain reaction or flow cytometry analysis. RVEC dysfunction was induced by tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) stimulation. The expression of cytokines, chemokines, adhesion molecules, and lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1 (LOX-1)/nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) was measured in RVECs with or without HCQ.
Results: HCQ treatment protected mice from uveitis, evidenced by reduced expression of inflammatory factors, chemokines, and adhesion molecules in the retina. In systemic immune response, HCQ inhibited the activation of naïve CD4+T cells and frequencies of T effector cells, and promoted T regulatory cells. HCQ decreased IRBP1-20-specific T cell responses and proliferation of CD4+T cells in vitro. Further studies established that TNF-α induced RVECs to express inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules, whereas HCQ alleviated the alterations via the LOX-1/NF-κB pathways.
Conclusions: HCQ alleviates EAU by regulating the Teff/Treg balance and ameliorating RVECs dysfunction via the LOX-1/NF-κB axis. HCQ may be a promising therapeutic candidate for uveitis.
Keywords: Hydroxychloroquine; T cells; experimental autoimmune uveitis; lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1 (LOX-1); nuclear factor κB (NF-κB); retinal vascular endothelial cells.
Copyright © 2022 Hu, Li, Chen, Li, Huang, Huang, Xie, Chen, Zhu, Wang, Chen, Su, Chen and Liang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activation of liver X receptor alleviates ocular inflammation in experimental autoimmune uveitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Apr 28;55(4):2795-804. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13323. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24699378 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin, an endogenous hormone, modulates Th17 cells via the reactive-oxygen species/TXNIP/HIF-1α axis to alleviate autoimmune uveitis.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 May 27;19(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02477-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 35624485 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein A1 Modulates Teff/Treg Balance Through Scavenger Receptor Class B Type I-Dependent Mechanisms in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Jul 8;63(8):23. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.8.23. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35881406 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-retina barrier dysfunction in experimental autoimmune uveitis: the pathogenesis and therapeutic targets.Anat Cell Biol. 2022 Mar 31;55(1):20-27. doi: 10.5115/acb.21.227. Anat Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35354673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Intraocular inflammation and homeostasis of the eye].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2009 Mar;113(3):344-77; discussion 378. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19348183 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the immunological interactions: targeting preeclampsia with Hydroxychloroquine's biological mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 5;15:1298928. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1298928. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38375029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An L-type calcium channel blocker nimodipine exerts anti-fibrotic effects by attenuating TGF-β1 induced calcium response in an in vitro model of thyroid eye disease.Eye Vis (Lond). 2024 Sep 6;11(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40662-024-00401-5. Eye Vis (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39237996 Free PMC article.
-
What can we learn from treatments of oral lichen planus?Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Feb 15;14:1279220. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1279220. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38426013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adrenomedullin-RAMP2 System Modulates Inflammation and Tissue Repair in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis Via T-Cell and M2 Macrophage Regulation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Jun 2;66(6):12. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.6.12. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40465267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caspi RR, Chan CC, Fujino Y, Najafian F, Grover S, Hansen CT, et al. . Recruitment of Antigen-Nonspecific Cells Plays a Pivotal Role in the Pathogenesis of a T Cell-Mediated Organ-Specific Autoimmune Disease, Experimental Autoimmune Uveoretinitis. J Neuroimmunol (1993) 47:177–88. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90028-W - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

