Exploring Macrophage-Dependent Wound Regeneration During Mycobacterial Infection in Zebrafish
- PMID: 35401552
- PMCID: PMC8987025
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.838425
Exploring Macrophage-Dependent Wound Regeneration During Mycobacterial Infection in Zebrafish
Abstract
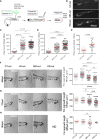
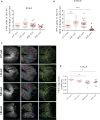
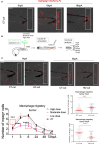
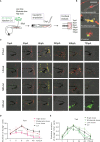
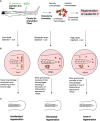
The molecular and cellular mechanisms associated with tissue degradation or regeneration in an infectious context are poorly defined. Herein, we explored the role of macrophages in orchestrating either tissue regeneration or degradation in zebrafish embryos pre-infected with the fish pathogen Mycobacterium marinum. Zebrafish were inoculated with different infectious doses of M. marinum prior to fin resection. While mild infection accelerated fin regeneration, moderate or severe infection delayed this process by reducing blastemal cell proliferation and impeding tissue morphogenesis. This was correlated with impaired macrophage recruitment at the wound of the larvae receiving high infectious doses. Macrophage activation characterized, in part, by a high expression level of tnfa was exacerbated in severely infected fish during the early phase of the regeneration process, leading to macrophage necrosis and their complete absence in the later phase. Our results demonstrate how a mycobacterial infection influences the macrophage response and tissue regenerative processes.
Keywords: Mycobacterium marinum; infection; macrophages sub-types; necrosis; regeneration; zebrafish.
Copyright © 2022 Bohaud, Johansen, Varga, Contreras-Lopez, Barthelaix, Hamela, Sapède, Cloitre, Gergely, Jorgensen, Kremer and Djouad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

