MILNP: Plant lncRNA-miRNA Interaction Prediction Based on Improved Linear Neighborhood Similarity and Label Propagation
- PMID: 35401586
- PMCID: PMC8990282
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.861886
MILNP: Plant lncRNA-miRNA Interaction Prediction Based on Improved Linear Neighborhood Similarity and Label Propagation
Abstract
Knowledge of the interactions between long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) is the basis of understanding various biological activities and designing new drugs. Previous computational methods for predicting lncRNA-miRNA interactions lacked for plants, and they suffer from various limitations that affect the prediction accuracy and their applicability. Research on plant lncRNA-miRNA interactions is still in its infancy. In this paper, we propose an accurate predictor, MILNP, for predicting plant lncRNA-miRNA interactions based on improved linear neighborhood similarity measurement and linear neighborhood propagation algorithm. Specifically, we propose a novel similarity measure based on linear neighborhood similarity from multiple similarity profiles of lncRNAs and miRNAs and derive more precise neighborhood ranges so as to escape the limits of the existing methods. We then simultaneously update the lncRNA-miRNA interactions predicted from both similarity matrices based on label propagation. We comprehensively evaluate MILNP on the latest plant lncRNA-miRNA interaction benchmark datasets. The results demonstrate the superior performance of MILNP than the most up-to-date methods. What's more, MILNP can be leveraged for isolated plant lncRNAs (or miRNAs). Case studies suggest that MILNP can identify novel plant lncRNA-miRNA interactions, which are confirmed by classical tools. The implementation is available on https://github.com/HerSwain/gra/tree/MILNP.
Keywords: label propagation; linear reconstruction; multilevel similarity; plant lncRNA-miRNA interaction; theoretical derivation.
Copyright © 2022 Cai, Gao, Ren, Fu, Xu, Wang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
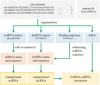
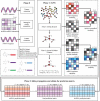
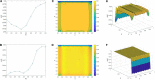
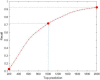
Similar articles
-
LncRNA-miRNA interaction prediction through sequence-derived linear neighborhood propagation method with information combination.BMC Genomics. 2019 Dec 20;20(Suppl 11):946. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6284-y. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31856716 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting lncRNA-disease associations based on combining selective similarity matrix fusion and bidirectional linear neighborhood label propagation.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Jan 19;24(1):bbac595. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac595. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 36592062
-
Multi-feature Fusion Method Based on Linear Neighborhood Propagation Predict Plant LncRNA-Protein Interactions.Interdiscip Sci. 2022 Jun;14(2):545-554. doi: 10.1007/s12539-022-00501-7. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Interdiscip Sci. 2022. PMID: 35040094
-
A Survey of Computational Methods and Databases for lncRNA-MiRNA Interaction Prediction.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2023 Sep-Oct;20(5):2810-2826. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2023.3264254. Epub 2023 Oct 10. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37030713 Review.
-
LMI-DForest: A deep forest model towards the prediction of lncRNA-miRNA interactions.Comput Biol Chem. 2020 Dec;89:107406. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107406. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Comput Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33120126 Review.
Cited by
-
lncRNA TUG1 and kidney diseases.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Mar 20;26(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04047-w. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40108517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aglawe S. B., Verma A. K., Upadhyay A. K. (2021). Bioinformatics tools and databases for genomics-assisted breeding and population genetics of plants: a review. Curr. Bioinform. 16 766–773.
-
- Ahmed S., Hossain Z., Uddin M., Taherzadeh G., Sharma A., Shatabda S., et al. (2020). Accurate prediction of RNA 5-hydroxymethylcytosine modification by utilizing novel position-specific gapped k-mer descriptors. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 18 3528–3538. 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.10.032 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amin N., McGrath A., Chen Y.-P. P. (2019). Evaluation of deep learning in non-coding RNA classification. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1 246–256. 10.1038/s42256-019-0051-2 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

