Exploring Genomic Variations in Nematode-Resistant Mutant Rice Lines
- PMID: 35401589
- PMCID: PMC8988285
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.823372
Exploring Genomic Variations in Nematode-Resistant Mutant Rice Lines
Abstract
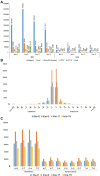
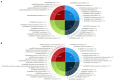
Rice (Oryza sativa) production is seriously affected by the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola, which has emerged as a menace in upland and irrigated rice cultivation systems. Previously, activation tagging in rice was utilized to identify candidate gene(s) conferring resistance against M. graminicola. T-DNA insertional mutants were developed in a rice landrace (acc. JBT 36/14), and four mutant lines showed nematode resistance. Whole-genome sequencing of JBT 36/14 was done along with the four nematode resistance mutant lines to identify the structural genetic variations that might be contributing to M. graminicola resistance. Sequencing on Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform identified 482,234 genetic variations in JBT 36/14 including 448,989 SNPs and 33,245 InDels compared to reference indica genome. In addition, 293,238-553,648 unique SNPs and 32,395-65,572 unique InDels were found in the four mutant lines compared to their JBT 36/14 background, of which 93,224 SNPs and 8,170 InDels were common between all the mutant lines. Functional annotation of genes containing these structural variations showed that the majority of them were involved in metabolism and growth. Trait analysis revealed that most of these genes were involved in morphological traits, physiological traits and stress resistance. Additionally, several families of transcription factors, such as FAR1, bHLH, and NAC, and putative susceptibility (S) genes, showed the presence of SNPs and InDels. Our results indicate that subject to further genetic validations, these structural genetic variations may be involved in conferring nematode resistance to the rice mutant lines.
Keywords: InDels; Meloidogyne graminicola; SNPs; genetic variations; genome; mutants; resistance; rice.
Copyright © 2022 Dash, Somvanshi, Godwin, Budhwar, Sreevathsa and Rao.
Conflict of interest statement
JG and RB were employed by Bionivid Technology Private Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A rice root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola-resistant mutant rice line shows early expression of plant-defence genes.Planta. 2021 Apr 17;253(5):108. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03625-0. Planta. 2021. PMID: 33866432
-
QTL mapping for resistance to and tolerance for the rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola.BMC Genet. 2018 Aug 6;19(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12863-018-0656-1. BMC Genet. 2018. PMID: 30081817 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and histological responses of African rice (Oryza glaberrima) to Meloidogyne graminicola provide new insights into root-knot nematode resistance in monocots.Ann Bot. 2017 Mar 1;119(5):885-899. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw256. Ann Bot. 2017. PMID: 28334204 Free PMC article.
-
Meloidogyne graminicola: a major threat to rice agriculture.Mol Plant Pathol. 2017 Jan;18(1):3-15. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12394. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017. PMID: 26950515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Region on Chromosome 7 Related to Differentiation of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Between Lowland and Upland Ecotypes.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jul 27;11:1135. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01135. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32849696 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Haplotype breeding: fast-track the crop improvements.Planta. 2025 Feb 1;261(3):51. doi: 10.1007/s00425-025-04622-3. Planta. 2025. PMID: 39891745 Review.
-
Distribution and Pathogenicity Differentiation of Physiological Races of Verticillium dahliae from Cotton Stems in Western China.Pathogens. 2024 Jun 21;13(7):525. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13070525. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39057752 Free PMC article.
-
The status of the CRISPR/Cas9 research in plant-nematode interactions.Planta. 2023 Oct 24;258(6):103. doi: 10.1007/s00425-023-04259-0. Planta. 2023. PMID: 37874380 Review.
References
-
- Basavaraju S. N., Lakshmikanth R. Y., Kumaraswamy R., Makarla U. (2020). Genotypes with enhanced expressions of acquired tolerance mechanisms showed improved growth under stress. Plant Physiol. Rep. 25, 9–23. doi: 10.1007/s40502-019-00482-8 - DOI
-
- Cabasan M. T. N., Kumar A., De Waele D. (2018). Evaluation of resistance and tolerance of rice genotypes from crosses of Oryza glaberrima and O. sativa to the rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola. Trop. Plant Pathol. 43, 230–241. doi: 10.1007/s40858-018-0210-8 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

