Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor Family Revealed Their Potential Roles in the Flowering Process in Longan (Dimocarpus longan)
- PMID: 35401601
- PMCID: PMC8990856
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.820439
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor Family Revealed Their Potential Roles in the Flowering Process in Longan (Dimocarpus longan)
Abstract
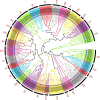
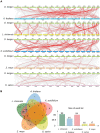
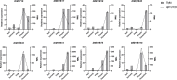
Longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) is a productive fruit crop with high nutritional and medical value in tropical and subtropical regions. The MYB gene family is one of the most widespread plant transcription factor (TF) families participating in the flowering regulation. However, little is known about the MYB TFs involved in the flowering process in longan and its regulatory network. In this study, a total of 119 DlR2R3-MYB genes were identified in the longan genome and were phylogenetically grouped into 28 subgroups. The groupings were supported by highly conserved gene structures and motif composition of DlR2R3-MYB genes in each subgroup. Collinearity analysis demonstrated that segmental replications played a more crucial role in the expansion of the DlR2R3-MYB gene family compared to tandem duplications, and all tandem/segmental duplication gene pairs have evolved under purifying selection. Interspecies synteny analysis among longan and five representative species implied the occurrence of gene duplication events was one of the reasons contributing to functional differentiation among species. RNA-seq data from various tissues showed DlR2R3-MYB genes displayed tissue-preferential expression patterns. The pathway of flower development was enriched with six DlR2R3-MYB genes. Cis-acting element prediction revealed the putative functions of DlR2R3-MYB genes were related to the plant development, phytohormones, and environmental stresses. Notably, the orthologous counterparts between Arabidopsis and longan R2R3-MYB members tended to play conserved roles in the flowering regulation and stress responses. Transcriptome profiling on off-season flower induction (FI) by KClO3 indicated two up-regulated and four down-regulated DlR2R3-MYB genes involved in the response to KClO3 treatment compared with control groups. Additionally, qRT-PCR confirmed certain genes exhibited high expression in flowers/flower buds. Subcellular localization experiments revealed that three predicted flowering-associated MYB proteins were localized in the nucleus. Future functional studies on these potential candidate genes involved in the flowering development could further the understanding of the flowering regulation mechanism.
Keywords: Dimocarpus longan; KClO3; R2R3-MYB; flower development; qRT-PCR.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Zhang, Fang, Wang, Xu, Zhao, Zhang and Fang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Borges R., Miguel E. C., Dias J. M. R., Da Cunha M., Bressan-Smith R. E., De Oliveira J. G., et al. (2004). Ultrastructural, physiological and biochemical analyses of chlorate toxicity on rice seedlings. Plant Sci. 166 1057–1062. 10.1016/j.plantsci.2003.12.023 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

